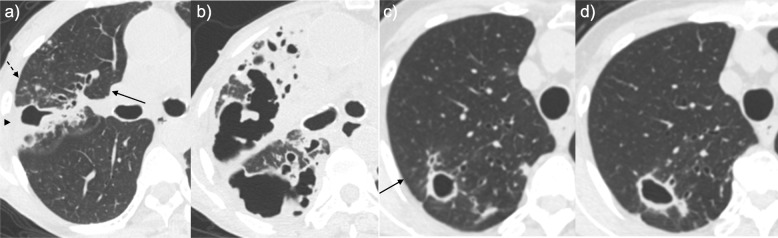
Fig. 1.
Typical computed tomography (CT) findings for Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary disease patients in this study. a, b A patient in the progressive cavity group. The follow-up period was 4.2 years. A) Initial CT scan (section thickness, 1 mm) showed cavity formation (maximum inner diameter, 22 mm) with consolidation (arrowhead), a small nodule, a nodule (dashed arrow), and bronchiectasis (arrow) in the right upper lobe. b Follow-up CT scan (section thickness, 1 mm) at a similar level showed extension of the cavity and emergence of new cavities. c, d A patient in the non-progressive cavity group. The follow-up period was 3 years. c Initial CT scan (section thickness, 1 mm) showed cavity formation (maximum inner diameter, 14 mm) with bronchiectasis (arrow) in the right upper lobe. d Follow-up CT scan (section thickness, 1 mm) at a similar level showed cavity formation (maximum inner diameter, 21 mm). All images show lung tissue (window width, 1500 Hounsfield units (HU); window level, − 600 HU)