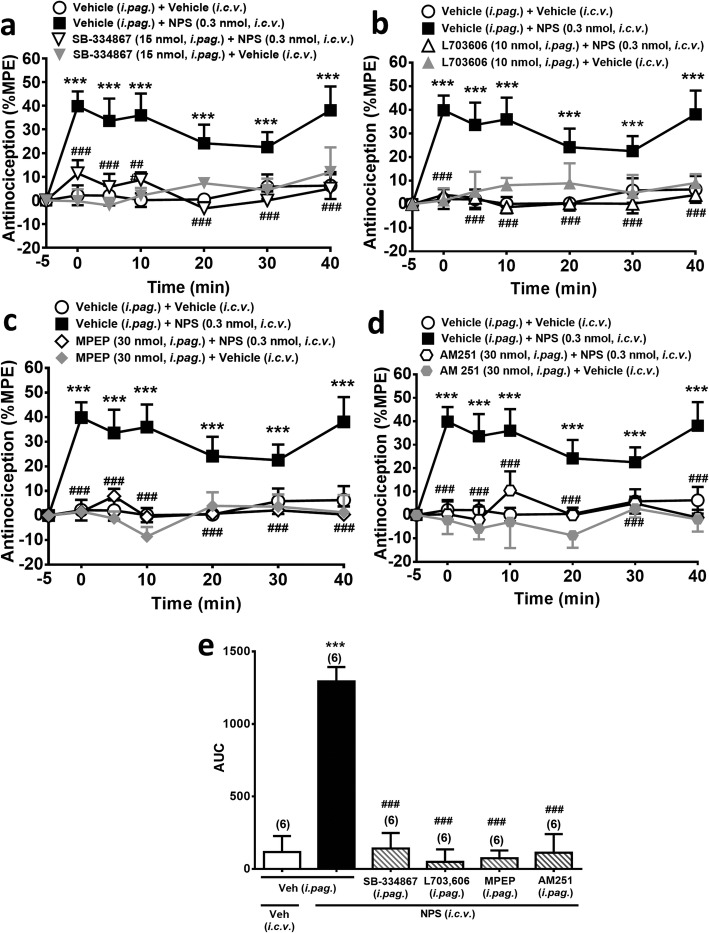
Fig. 5.
NPS (i.c.v.)-induced antinociception is antagonized by i.pag. blockade of OX1Rs, NK1Rs, mGlu5Rs or CB1Rs. a-d: Time courses of antinociceptive effects (expressed as % MPE) induced by NPS (0.3 nmol, i.c.v.) in combination with the vehicle or the antagonists of OX1Rs (SB-334867, 15 nmol, i.pag.), NK1Rs (L-703,606, 10 nmol, i.pag.), mGlu5Rs (MPEP, 30 nmol, i.pag.) or CB1Rs (AM251, 30 nmol, i.pag.) in the mouse hot-plate test. (two-way ANOVA /post hoc Bonferroni test). e: The AUC of the antinociceptive effect in each treatment group (one-way ANOVA /post hoc Tukey test). The antagonist was i.pag. Administered immediately before i.c.v. injection of NPS. The data presentation and statistics are the same as in Fig. 2. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. the vehicle control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. the NPS group