Figure 8.
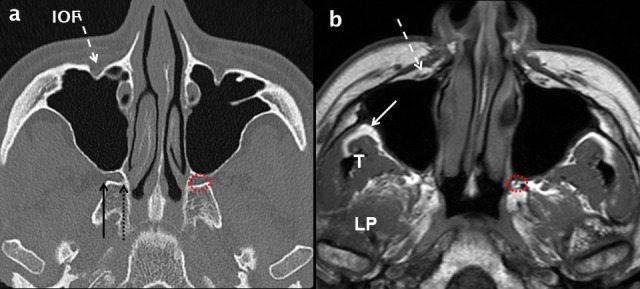
Normal axial anatomy at the mid maxillary sinus level. Comparative axial MDCT (a) and T1 weighted MRI (b) images through the mid maxillary sinus level demonstrating bone and soft-tissue anatomy. The infra orbital neurovascular complex (white dashed arrows) is shown within the IOF. Peripheral to the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, the infratemporal fossa (white arrow in b) is an important deep fascial space. The muscles of the medial aspect of the masticator space: temporalis (T) and LP are shown (b). The PPF (dotted red circle in a and b) contains fat, vessels and nerves. Its lateral boundary is the pterygomaxillary fissure (solid black arrow in a) which communicates with the infratemporal fossa. At the superomedial margin of the PPF is the sphenopalatine foramen (dotted black arrow in a) which is in continuity with the nasal cavity. IOF:infraorbital foramen; LP: lateral pterygoid; MDCT: multidetector CT; PPF: pterygopalatine fossa.
