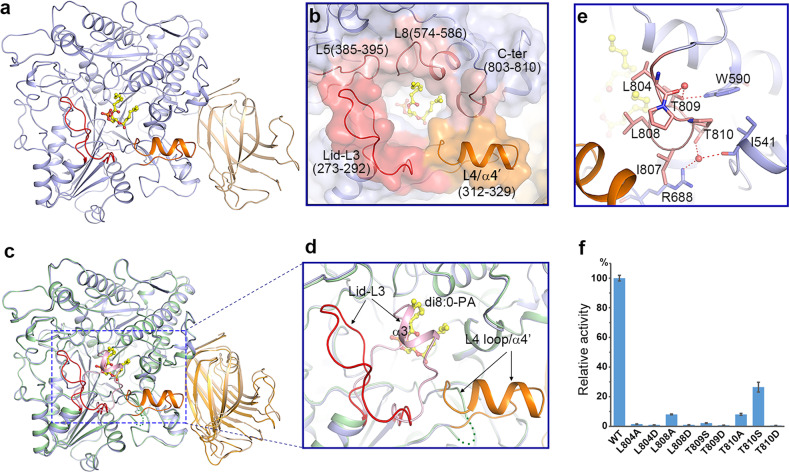
Fig. 3.
Substrate-binding pocket and conformational changes induced by substrate binding. a Ribbon structure of PLDα1 in complex with di8:0-PA. The catalytic domain and C2 domain are colored in slate blue and wheat, respectively. The Lid L3 loop, and pocket-forming L4 loop/α4′ are colored in red and orange, respectively. The di8:0-PA molecule is shown as a yellow stick model. b Zoom-in view shows the substrate-binding pocket. Among structure elements constituting the substrate-binding pocket, the L3 loop is colored in red, the L4 loop and α4′ are colored in orange, and the L5/L8 loops and the C-terminus 310 helix are colored in pink. c Structure superimposition of PLDα1 structure in apo form (the catalytic domain, C2 domain, and the substrate-binding pocket Lid-α3′ are colored in pale green, bright orange and light pink, respectively) and PA-binding form (colored codes are the same as in a) shows the conformational changes. The L4 loop (green dotted line) in the apo structure turns into α4′ helix (colored in orange) upon PA binding. d Zoom-in view of the substrate-binding pocket region showing conformational changes. e Interaction of the C-terminus with surrounding residues. The side chains of the interaction residues are shown with sticks, and water molecules are shown with red spheres. Red dotted lines indicate the hydrogen-bonding interactions. f Influence of C-terminal residue mutations on PLDα1 activity. Results are means ± SD, n = 3