Table 2.
Approved Drugs.
| Compound | Company | Structure | Mechanism of Action | Formulations | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyurea | Numerous | Hydroxycarbamide CH4N2O2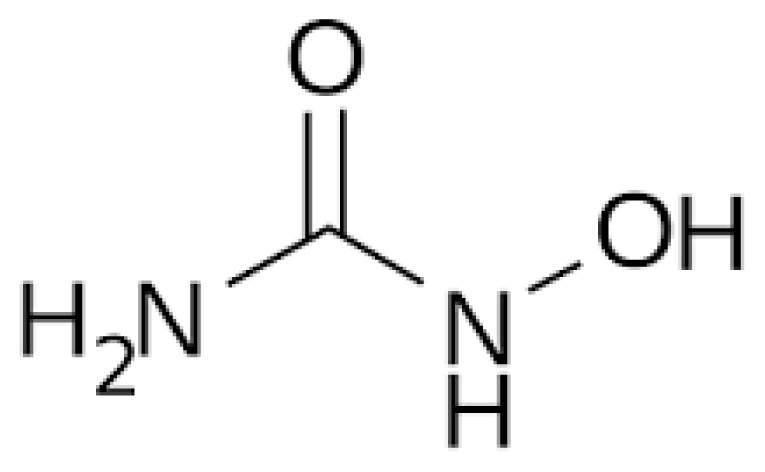
|
An antineoplastic agent that inhibits DNA synthesis through the inhibition of ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase. Hb F Induction, reduces inflammation and hemolysis | Capsules: Hydrea and Droxia; 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 mg Tablets: Siklos;100 mg, 1000 mg Solution 100 mg/ml or higher as needed |
Sickle cell anemia; Myeloproliferative disorders, certain cancers |
| L-Glutamine (Endari) | Emmaus Medical Inc. | 2-Amino-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid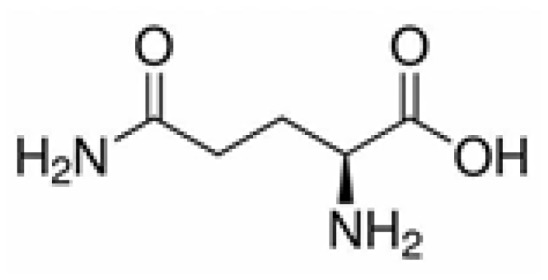
|
Not well known. It may improve the NAD redox potential in sickle RBCs through increasing the availability of reduced glutathione. | Powder in packets containing 5g each | Reduction of the acute complications of sickle cell disease in adult and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older |
| Crizanlizumab-tmca | Novartis | Monoclonal antibody | Anti-P-selectin | Intravenous solution | Reduces the frequency of VOCs in adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older |
| Voxelotor (Oxbryta, GBT440) | Global Blood Therapeutics Inc | Benzaldehyde, 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)methoxy)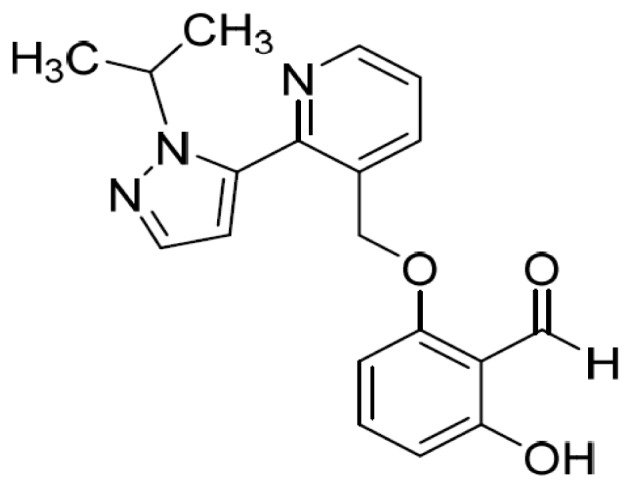
|
Hb S Polymerization inhibitor | Tablets (500 mg) for oral use | Treatment of sickle cell disease in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older |
NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotid.
