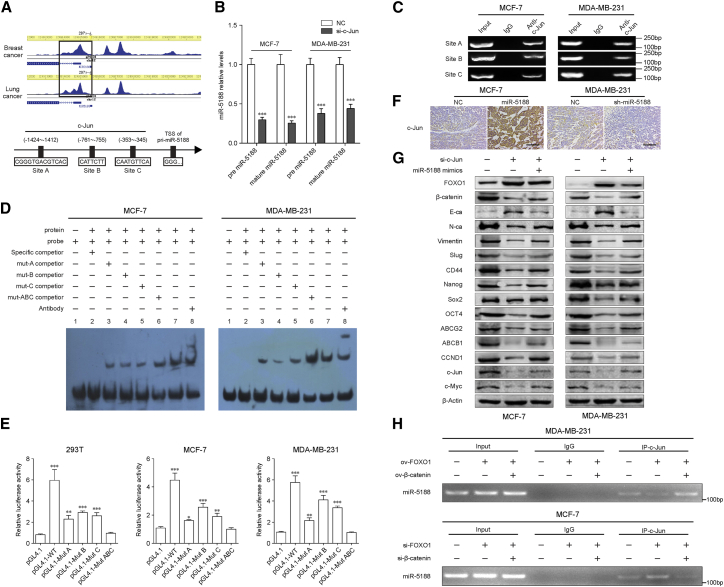
Figure 6.
c-Jun Transcriptionally Promotes miR-5188 Expression to Form a Positive Regulatory Loop
(A) ChIP-seq binding peaks were searched using the Cistrome data browser, and bioinformatics analysis were performed to identify binding sites of c-Jun within the miR-5188 promoter. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of pre-miR-5188 and mature miR-5188 expression in c-Jun-depleted MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells and their control cells. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis verified c-Jun binding to the miR-5188 promoter. (D) The protein-DNA interaction between c-Jun and miR-5188 promoter was determined using the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (E) Luciferase reporter assays were performed to confirm c-Jun binding to the miR-5188 promoter. (F) Immunohistochemistry analysis of c-Jun expression in xenograft tumors derived from MCF-7 cells after stable miR-5188 overexpression, MDA-MB-231 cells after stable miR-5188 knockdown, and their controls (scale bars, 40 μm) (n = 5). (G) Western blot analysis of stemness, metastasis, proliferation, chemoresistance, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated protein expression in c-Jun-silenced MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells, miR-5188-overexpressed MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells, c-Jun-silenced MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells with miR-5188 overexpression, and their control cells. (H) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of c-Jun binding to miR-5188 promoter in FOXO1-overexpressed MDA-MB-231 cells, FOXO1-overexpressed MDA-MB-231 cells with β-catenin overexpression, FOXO1-silenced MCF-7 cells, FOXO1-silenced MCF-7 cells with β-catenin knockdown, and their control cells. ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.