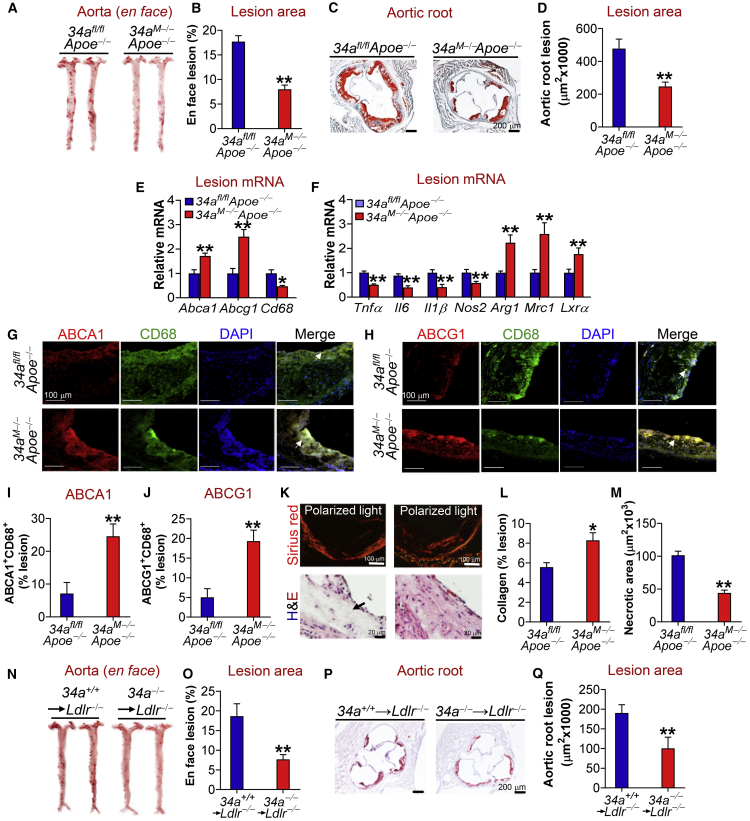
Figure 3.
Macrophage- or Myeloid-Selective miR-34a Ablation Protects against Atherosclerosis in Apoe−/− or Ldlr−/− Mice
(A–M) 34afl/flApoe−/− or 34aM−Apoe−/− mice were fed a Western diet for 18 weeks. En face aortas were stained by oil red O (ORO) (A), and the plaque size was quantified (B) (n = 15–17). Aortic roots were sectioned and stained with ORO (C), and the plaque size was determined (D) (n = 14–16). The mRNA levels of genes in the plaques of aortic roots were quantified by quantitative real-time PCR (n = 6) (E and F). The proteins in aortic roots were detected by immunohistochemistry (G and H), and ABCA1 (I) or ABCG1 (J) protein levels in the macrophages of plaques were quantified (n = 5). Negative controls are presented in Figure S8A. Collagens in the aortic roots were stained with picro sirius red (K; top panel), and the collagen content in plaques was quantified (L) (n = 5). In addition, aortic roots were stained with H&E (K; bottom panel), and the necrotic size in the plaques was analyzed (M) (n = 5). (N–Q) Bone marrow from miR-34a+/+ or miR-34a−/− mice was transplanted into irradiated Ldlr−/− mice, which were then fed a Western diet for 16 weeks. En face aortas were stained with ORO (N), and the plaque size was determined (O) (n = 9–12). Aortic roots were also stained by ORO (P), and the plaque size was determined (Q) (n = 9–10). See also Figures S7 and S8. In (G) and (H), arrows point to ABCA1+CD68+ cells (G) or ABCG1+CD68+ cells (H). In (K), the arrow points to the necrotic area. All of the data are expressed as mean ± SEM. A two-tailed Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.