Figure 5.
Global Loss of miR-34a Inhibits Lipid Absorption via Inhibiting Hepatic CYP7A1 and CYP8B1 Expression
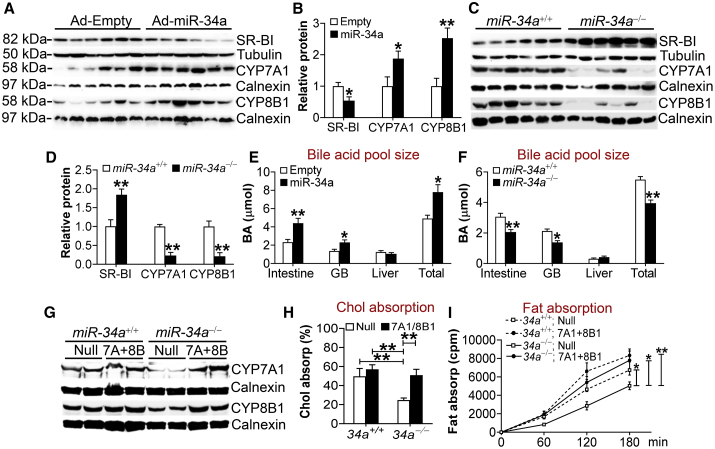
(A and B) C57BL/6 mice were injected i.v. with Ad-Empty or Ad-miR-34a. After 7 days, hepatic proteins were used for immunoblotting assays (A), and protein levels were quantified (B) (n = 6). (C and D) Hepatic proteins were isolated from chow-fed miR-34a+/+ or miR-34a−/− mice (n = 6). Western blotting assays were performed (C), and hepatic protein levels were quantified (D). (E and F) Bile acid levels in mice infected with Ad-Empty or Ad-miR-34a (E) or in chow-fed miR-34a+/+ or miR-34a−/− mice (F) (n = 7–8). (G–I) miR-34a+/+ or miR-34a−/− mice were fed a Western diet for 18 weeks and then injected i.v. with Ad-Empty (Null) or Ad-CYP7A1 plus Ad-CYP8B1 (7A+8B). After 7 days, hepatic proteins were used for immunoblotting assays (G), and intestinal cholesterol (H) or fat (I) absorption was determined (n = 7–8). See also Figure S12. All of the data are expressed as mean ± SEM. In (A)–(F), a two-tailed Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. In (H) and (I), a two-way ANOVA test was used for statistical analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.