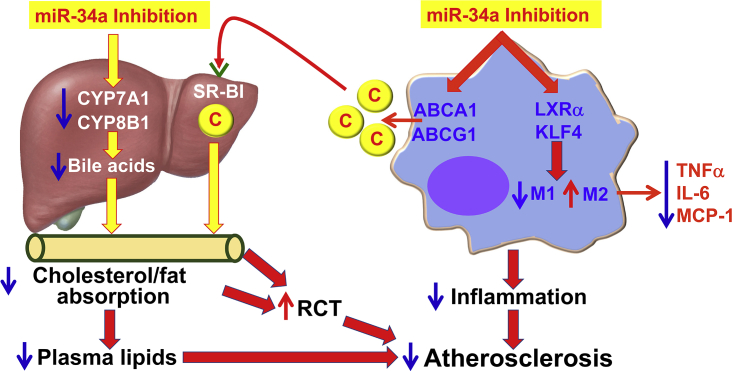
Figure 7.
A Model for Macrophage miR-34a to Regulate Atherogenesis
Inhibition of macrophage miR-34a induces ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression to promote macrophage cholesterol efflux. HDL carries the effluxed free cholesterol to the liver by binding to SR-BI. In the liver, free cholesterol is secreted to the bile and then to the intestine. miR-34a inhibition also suppresses hepatic CYP7A1 and CYP8B1 expression, resulting in a reduction in bile acid synthesis in the liver, as well as cholesterol and fat absorption in the intestine. As a result, reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is increased and plasma lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) are decreased. On the other hand, miR-34a inhibition also induces LXRα and KLF4 to promote M2 macrophage polarization, thus reducing macrophage inflammation. By reducing macrophage inflammation and inducing macrophage cholesterol efflux and RCT, inhibition of miR-34a can both prevent and regress atherosclerosis. C, cholesterol.