Figure 6.
SiC Vector Application in Mouse
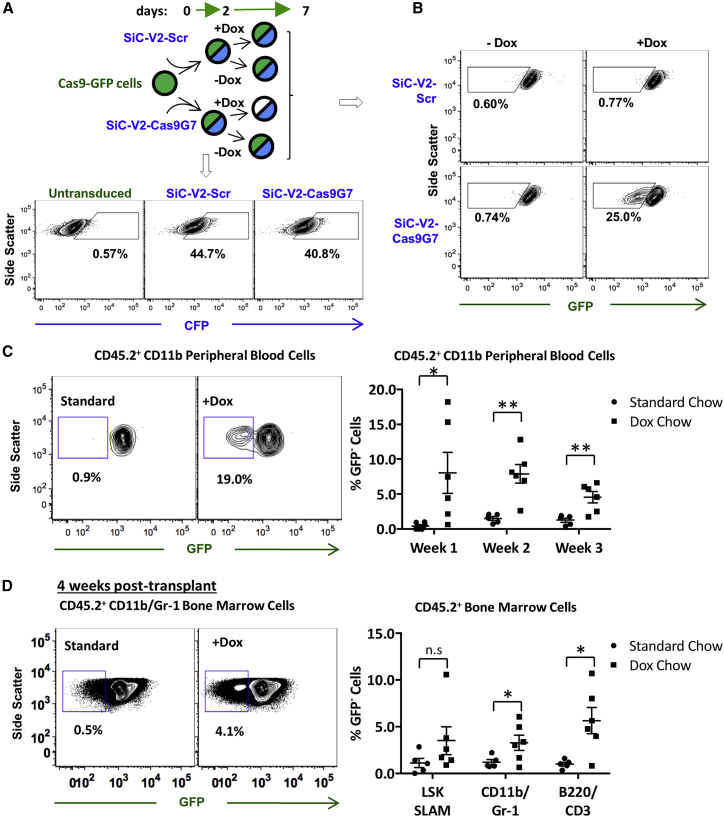
(A) HSPCs isolated from transgenic Cas9-EGFP mouse bone marrow were transduced with SiC-V2-Scr (control) or SiC-V2-Cas9G7 at ∼40%–45% efficiency (based on CFP signal). 1 μg/mL Dox was added to a portion of the cells on day 2. (B) Cytometry analysis at day 7 shows 25% Cas9 editing (i.e., low GFP signal) upon Dox treatment of SiC-V2-Cas9G7 transduced cells. (C and D) Donor Cas9-EGFP mouse HSPCs (CD45.2+) transduced with SiC-V2-Cas9G7 overnight were transplanted into recipient B6.SJL (CD45.1+) mice. Animals received standard (n = 5) or Dox chow (n = 6). (C) Flow cytometry analysis was performed on peripheral blood cells 1 to 3 weeks post-transplant. Representative dot plot of CD45.2+ CD11b+ peripheral blood cells 1 week post-transplant (left). Percent GFP− CD45.2+ CD11b+ cells at different times in mice fed with standard or Dox chow (right). (D) Bone marrow was analyzed at 4 weeks. Representative dot plot showing appearance of GFP− CD45.2+ CD11b+/Gr-1+ granulocytes upon Dox treatment (left). GFP− CD45.2+ LSK SLAM, CD11b/Gr-1, and B220/CD3 cells in mice fed with standard or Dox chow (right). *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01 (Student’s unpaired, two-tailed t tests). See also Figure S5.