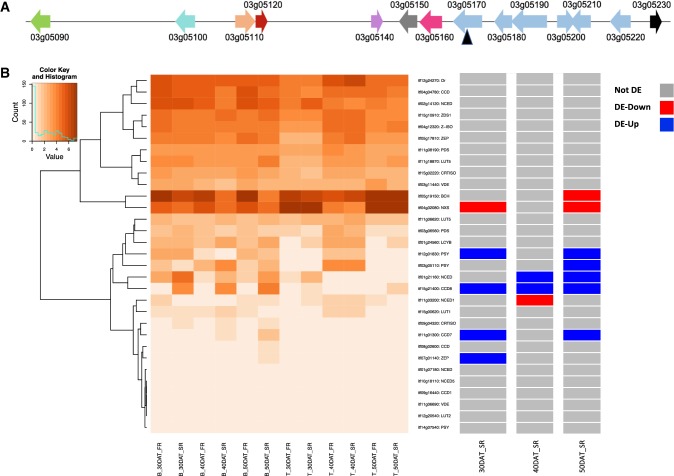
Fig. 4.
Characterization of the QTL on LG3 underlying starch and β-carotene. a Genes are noted by arrows: Homeodomain-like superfamily protein (green); sucrose synthase (aqua), phytoene synthase (lt. orange), glutathione S-transferase (burgundy), AMP-dependent synthetase and ligase family protein (lilac), RAB homolog (gray), polyamine oxidase (magenta), P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase superfamily protein (Lt. blue), and conserved hypothetical (black). Black arrowhead denotes marker S3_3185578. b Left panel: Expression abundances (log2 fragments per kilobase per exon model per million mapped reads (FPKM)) of candidate genes involved in carotenoid metabolism are shown in the heat map below each gene for Beauregard (B) and Tanzania (T) for storage roots (SR) and fibrous roots (RF) at 30, 40, and 50 days after transplanting (DAT). Key code value indicates log2 FPKM and count indicates the number of samples (sample = one gene per sampling) with that FPKM value shown as a histogram. Gene identifiers and gene name abbreviations are listed to the right of the heat map. BCH, β-carotene hydrolase; CCD, carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases; CRTISO, carotene isomerase; LUT, lutein deficient; LYCB, lycopene b-cyclase; NCED, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase; NXS, neoxanthin synthase; OR, ORANGE protein; PDS, phytoene desaturase; PSY, phytoene synthase; VDE, violaxanthin de-epoxidase; ZEP, zeaxanthin epoxidase; ZDS, zeta-carotene desaturase; Z-ISO, z-carotene isomerase. Right panel: Differentially expressed genes based on the comparison of Beauregard versus Tanzania storage roots (color figure online)