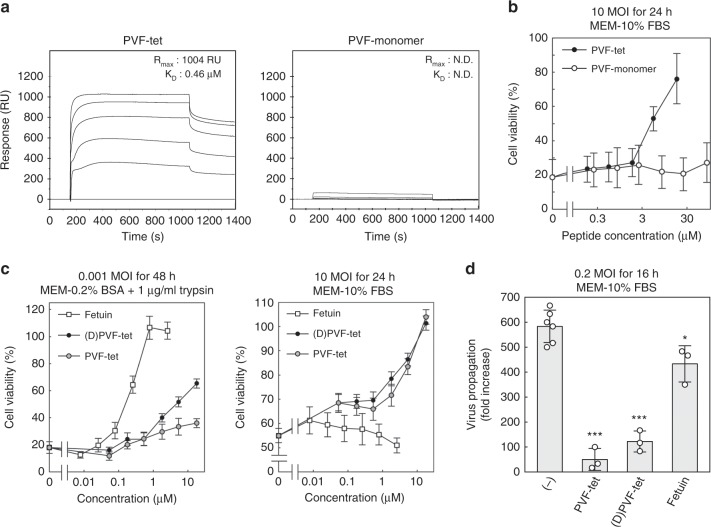
Fig. 2. PVF-tet functions based on the clustering effect, especially under a high MOI.
a Kinetics of the binding of PVF-tet or its monomer peptide to immobilized HA analyzed using the BIAcore system. The resonance unit (RU) is an arbitrary unit used by the BIAcore system to indicate peptide binding. b The effects of PVF-tet or its monomer peptide on the cytopathicity induced by IAV infection. MDCK cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of each compound for 30 min, and then infected with IAV strain PR8 at 10 MOI for 24 h in the presence of the indicated amounts of each peptide. Data are presented as a percentage of the control value without infection (mean ± SEM of three independent experiments). c The effects of fetuin or each tetravalent peptide on the cytopathicity induced by IAV infection. MDCK cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of each compound for 30 min, and then infected with IAV strain PR8 at 0.001 MOI in the presence of 1 μg/ml trypsin for 48 h (left panel) or 10 MOI in the absence of trypsin for 24 h (right panel). Data are presented as a percentage of the control value without infection (mean ± SEM of three independent experiments). d The effect of fetuin (7.8 μm) or each tetravalent peptide (60 μm) on virus propagation after IAV infection. MDCK cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of each compound for 30 min, and then infected with IAV strain PR8 at 0.2 MOI for 16 h. The virus titer in the supernatant was determined by a plaque assay. Data are presented as a fold increase over the initial virus titer (60,000 pfu/ml) (mean ± SD of 3–6 independent experiments). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 (compared with no compound (−) treatment by ANOVA followed by one-sided Dunnett’s test). Experimental details are shown above each panel. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.