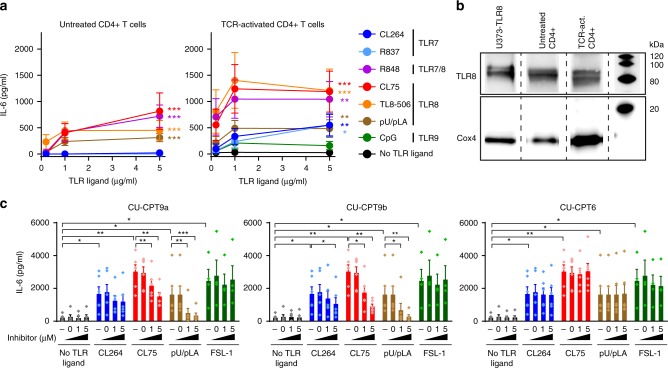
Fig. 2. TLR8 is expressed and induces secretion of IL-6 in human primary CD4+ T cells.
a Untreated or TCR-activated human primary CD4+ T cells were stimulated with 0.2, 1, and 5 μg/ml ligands to TLR7 (CL264, R837), TLR7/8 (R848), TLR8 (CL75, TL8-506, pU/pLA), or TLR9 (CpG, 0.2, 1, 5 μM) for 24 h and IL-6 secretion was analyzed by ELISA. Data represent mean + SEM from four independent experiments. b TLR8 expression in untreated or TCR-activated CD4+ T cells was analyzed by immunoblotting. Lysates from U373 cells overexpressing human TLR8 were used as positive control and Cox4 as housekeeping control. c CD4+ T cells were untreated (−) or pre-treated with DMSO (=0), 1 or 5 μM of TLR8-specific inhibitors CU-CPT9a, CU-CPT9b, or the negative control compound CU-CPT6, for 2 h prior to TCR activation and stimulation with 5 μg/ml CL264, CL75, pU/pLA, or FSL-1 (TLR2) for 24 h. IL-6 secretion was analyzed by ELISA. Bars represent mean + SEM from six independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined in a by calculating areas under the curve (AUC) followed by repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Dunnett´s post-test on log-transformed data, in c by two-way ANOVA with Dunnettʼs post-test; significance levels: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data File.