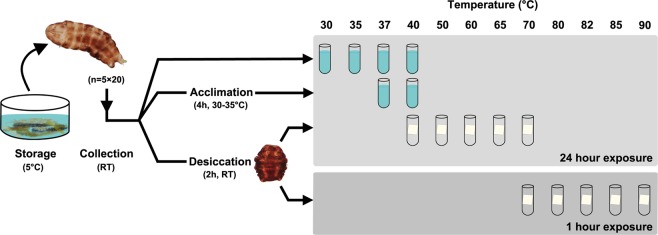
Figure 2.
A graphical representation of the methods used to evaluate the effect of exposures to high temperature in active as well as desiccated tardigrades. Active specimens were randomly pooled into groups (5 × ca. 20) at room temperature (RT) and then: (i) exposed to high temperature (30, 35, 37 and 40 °C) for 24 hours or, (ii) briefly acclimated (2 hours at 30 °C followed by 2 hours at 35 °C) and exposed to 37 and 40 °C for a 24 hour period. To assess thermotolerance of anhydrobiotic tuns, tardigrades were also randomly pooled into groups (5 × ca. 20), then desiccated and exposed to high temperature for either 24 hour (40, 50, 60, 65 and 70 °C) or 1 hour (70, 80, 82, 85 and 90 °C).