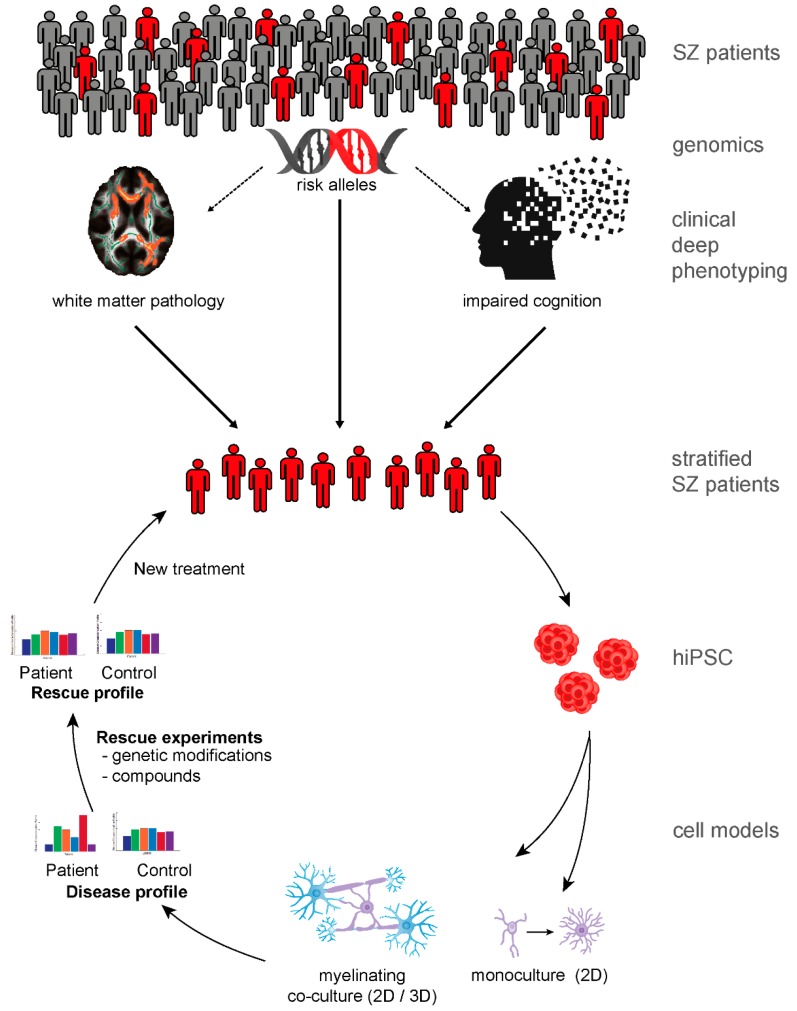
Figure 1.
Principals of patient stratification for subsequent human-induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-based cellular disease modeling and new treatment strategies. Stratification of schizophrenia (SZ) patients could be based on genetics or endophenotypes or a combination of the two. Recent evidence suggests that patients with oligodendrocyte dysfunction and white matter pathology have cognitive impairments. Red human icons illustrate patients who are risk gene carriers with the shared endophenotypes of disturbed white matter pathology and impaired cognition. Meaningful patient stratification based on genomics and clinical deep phenotyping enables subsequent investigations of underlining cellular and molecular mechanisms. hiPSC technology enables the generation of a toolbox of patient-derived cell models. Monocultures of glial cells and myelinating co-culture systems could simulate disease-relevant endophenotype profiles of SZ in vitro. Moreover, hiPSC-derived models can be used for genetic and pharmacological rescue experiments and pave the way for new treatment options. Aspects or parts of the illustrations have been published previously [93,111].