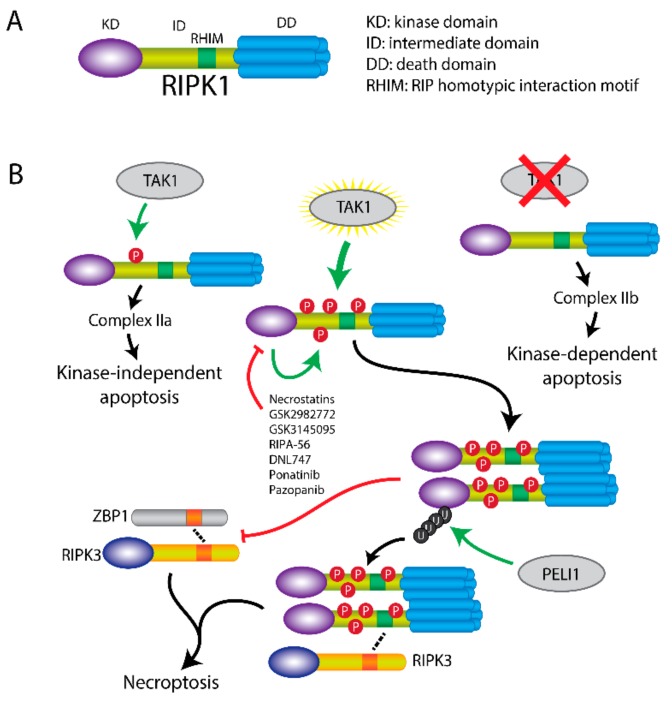
Figure 2.
Cell death induction by RIPK1 regulation. (A) Scheme of RIPK1 structure. RIPK1 consists of an N-terminal kinase domain (KD), a RHIM containing intermediate domain (ID), and a C-terminal death domain (DD). (B) RIPK1-mediated cell death is regulated by TAK1. TAK1-induced phosphorylation of ID domain within RIPK1 initiates RIPK1-independent apoptosis via complex IIa. In the absence of TAK1, RIPK1-dependent apoptosis is induced via complex IIb. When RIPK1 is hyperphosphorylated by TAK1, RIPK3-dependent necroptosis is induced through DD dimerization. Necroptosis can be inhibited by RIPK1 inhibitors, such as necrostatins, GSK2982772, GSK3145095, RIPA-56, DNL747, ponatinib and pazopanib. E3-ligase PELI1 induces polyubiquitination of RIPK1, which in turn regulates the interaction of RIPK1 with RIPK3 and promotes necroptosis. Besides induction of cell death, RIPK1 also exerts necroptosis-inhibitory functions by inhibiting RIPK3 activation through other RHIM containing proteins, such as ZBP1.