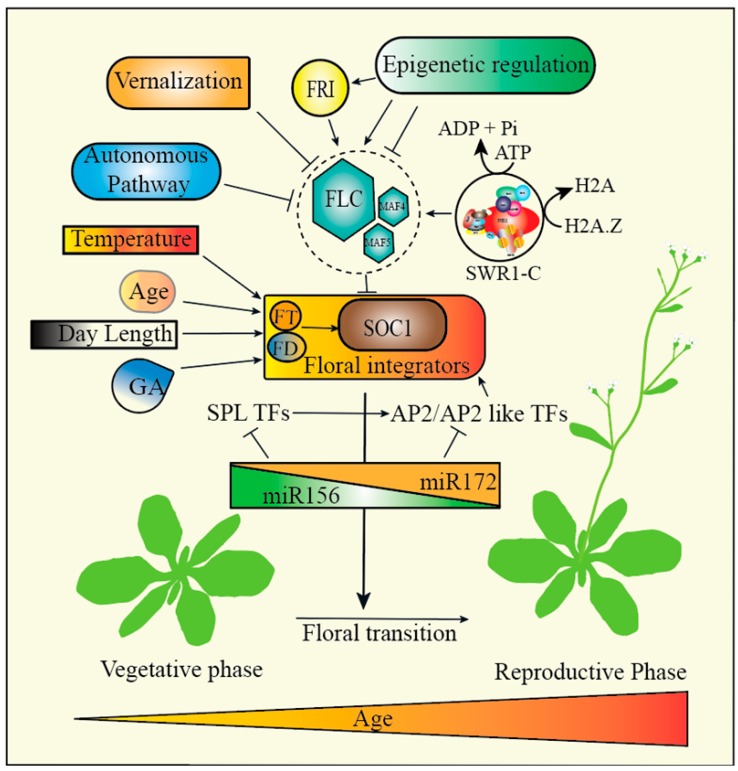
Figure 2.
Regulation of flowering time in Arabidopsis. FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), plays a key role in flowering time induction by acting as a repressor of flowering. The expression of FLC is regulated by FRIGIDA, vernalization, autonomous pathways, and SWR1-C. FLC restricts flowering by directly repressing the key genes responsible for flowering including FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), FD, and SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1). The vernalization pathway promotes flowering in response to the prolonged exposure to cold temperature by turning off the FLC. Flowering can also be induced by age, photoperiod, and Gibberellic acid (GA). The photoperiod promotes flowering in response to day length. Additionally, miR156/miR172 also play a critical function in phase change by targeting the transcription factors SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) and APETALA2 (AP2) like genes.