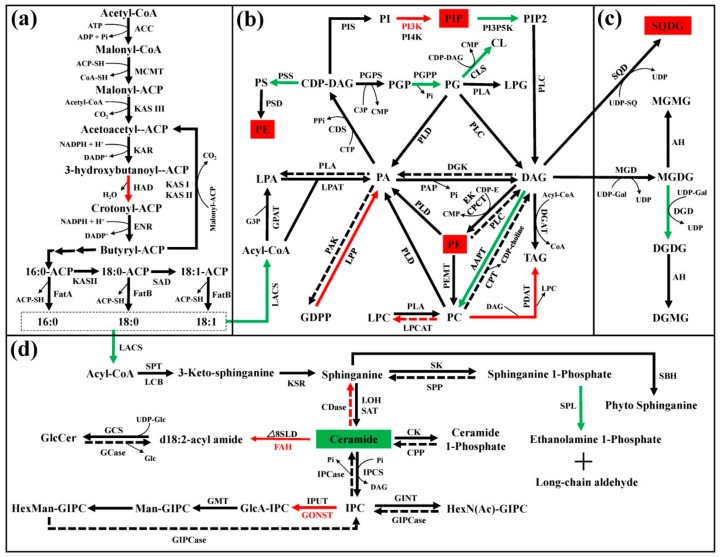
Figure 8.
Influence of ethylene on amount of compounds and expression of genes in lipid pathway in peach. The pathway includes four parts as fatty acid biosynthesis (a), phospholipid metabolism (b), galactolipid metabolism (c), and sphingolipid metabolism (d). The red arrows indicate promotive effect of ethylene on transcript levels; the green arrows indicate the inhibitive effect of ethylene on transcript levels. Solid arrows indicate biosynthetic steps and dashed ones indicate catabolic steps. The red box indicates lipid with content significantly higher in ethylene treated fruit; the green box indicates lipid with content significantly lower in ethylene treated fruit (p < 0.05) according to Duncan’s multiple range test. Δ8SLD, delta8 sphingolipid long-chain base desaturase; AAPT, aminoalcohol phosphotransferases; ACC, acetyl CoA carboxylase; ACP-SH, acyl carrier protein- sulfhydryl; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AH, acetylhydrolase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CDase, ceramidase; CDP-DAG, cytidine diphosphate (CDP)-diacylglycerol (DAG); CDP-E, CDP- ethanolamine; CDS, CDP-diacylglycerol synthase; Cer, ceramide; CK, ceramide kinase; CL, cardiolipin; CLS, CL synthase; CMP, cytidyl monophosphate; CoA, coenzyme A; CoA-SH, coenzyme A-sulfhydryl; CPCT, CTP (cytidine 5′-triphosphate): phosphoethanolamine cytidylyltransferase; CPP, ceramide 1-phosphate phosphatase; CPT, diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DGAT, DAG acyltransferase; DGD, digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase; DGDG, digalactosyldiacylglycerol; DGK, DAG kinase; DGMG, digalactosylmonoacyglycerol; DGPP, diacyglycerol pyrophosphate; EK, ethanolamine kinase; ENR, enoyl-ACP reductase; FAD, fatty acid desaturase; FAH, fatty acid alpha-hydroxylase; FatA, Fatty acid thioesterase A; FatB, Fatty acid thioesterase B; G3P, glycerol-3-phosphate; Gal, galactose; GCase, glucosylceramidase; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; GINT, glucosamine inositolphosphorylceramide transferase; GIPC, glycosyl inositol phosphoceramide; GIPCase, glycosylinositolphosphoceramidase; Glc, glucose; GlcCer, glycosyl ceramide; GMT, GIPC mannosyl-transferase; GONST, golgi-localized nucleotide sugar transporter; GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; HAD, hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydrase; HexNAc, nacetylhexosamine; IPC, inositolphosphorylceramide; IPCS, IPC synthase; IPUT, inositol phosphoryl ceramide glucuronosyltransferase; KAR, ketoacyl-ACP reductase; KASI, ketoacyl-ACP synthase I; KASII, ketoacyl-ACP synthase II; KASIII, ketoacyl-ACP synthase III; KSR, ketosphinganine reductase; LACS, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; LCB, sphingolipid Δ8 long-chain base; LOH, lag1 longevity assurance homolog; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPAT, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPCAT, LPC acyltransferase; LPP, lipid phosphate phosphatase; Man, mannose; MCMT, malonyl-CoA: ACP malonyltransferase; MGD: monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase; MGDG, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; MGMG, monogalactosylmonoacylglycerol; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAK, PA kinase; PAP, PA phosphatase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PDAT, PC: DAG acyltransferase; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PEMT, PE methyltransferase; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PGP, PG phosphate; PGPP, PGP phosphatase; PGPS, PGP synthase; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PI3K, PI 3-kinase; PI3P5K, PI-3-phosphate-5-kinase; PI4K, PI 4-kinase; PIP, PI phosphate; PIP2, PI bisphosphate; PIS, phosphoinositide synthase; PLA, phospholipase A; PLC, phospholipase C; PLD, phospholipase D; PPi, inorganic diphosphate; PS, phosphatidylserine; PSD, PS decarboxylase; PSS, base-exchange-type phosphatidylserine synthase; SAD, stearoyl-ACP desaturase; SAT, sphingosine N-acyltransferase; SBH, sphingosine base hydroxylase; SK, sphingosine kinase; SPL, sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase; SPP, sphingosine phosphate phosphatase; SPT, serine palmitoyltransferase; SQ, sulfoquinovose; SQD, UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase; SQDG, sulfoquinovosyldiacyglycerol; UDP, uridine 5′-diphosphate; TAG, triacyl glycerol.