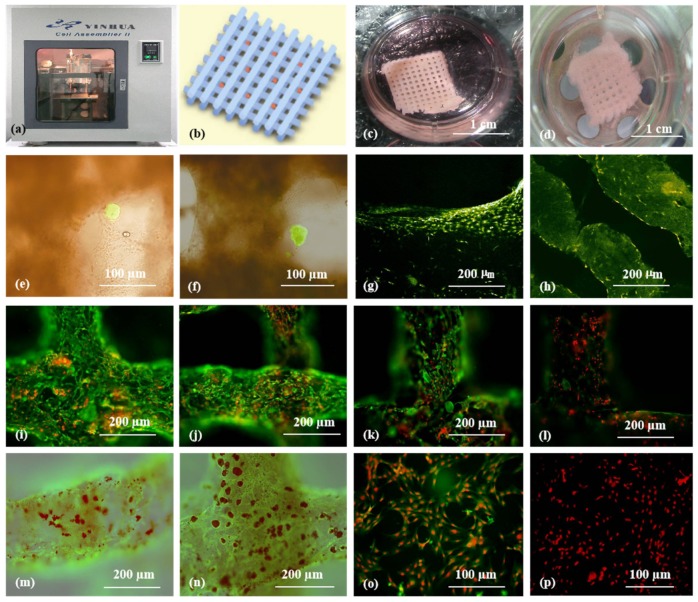
Figure 8.
3D bioprinting of ASC-laden gelatin/alginate/fibrin hydrogel for organ manufacturing in Prof. Wang’s laboratory at Tsinghua University: (a) a pioneering double-nozzle 3D bioprinter made in this laboratory; (b) schematic description of the cell-laden gelatin/alginate/fibrin hydrogel and pancreatic islets being printed into a grid construct using the 3D bioprinter; (c) a large-scale 3D printed grid construct containing ASC-laden gelatin/alginate/fibrin hydrogel cultured in a plate; (d) a grid ASC-laden gelatin/alginate/fibrin construct after being cultured for one month; (e) a multicellular construct after three weeks of culture, containing both ASCs encapsulated in the gelatin/alginate/fibrin hydrogel before epidermal growth factor (EGF) engagement and relatively integrated pancreatic islets seeding in the predefined channels (immunostaining with anti-insulin in green); (f) some envelopes of the islets were broken after one month of culture; (g) immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD31+ cells (i.e., mature endothelial cells from the ASC differentiation after three days of culture with EGF added in the culture medium) in green, having a fully confluent layer of endothelial cells (i.e., endothelium) on the surface of the predefined channels; (h) a vertical image of the 3D construct showing the fully confluent endothelium (formed from endothelial cells) and the predefined go-through channels; (i) immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD34+ cells (i.e., endothelial cells) in green and pyrindine (PI) for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red; (j) immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD34+ endothelial cells in green and PI for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red after three days of culture without EGF added in the culture medium; (k) immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD31+ endothelial cells in green and PI for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red after three days of culture with EGF added in the culture medium; (l) a control of (k), immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD31+ endothelial cells differentiated from the ASCs in green and PI for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red after three days of culture without EGF added in the culture medium; (m) immunostaining of the 3D construct with mAbs for CD31+ cells in green and Oil Red O staining for adipocytes in red, showing both the heterogeneous tissues coming from the ASC differentiation after a cocktail growth factor engagement (i.e., on the surface of the channels, the endothelium coming from the ASCs differentiation after being treated with EGF for 3 days; deep inside the gelatin/alginate/fibrin hydrogel, the adipose tissue coming from the ASC differentiation after being subsequently treated with insulin, dexamethasone, and isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX) for another three days); (n) a control of (m), showing all the ASCs in the 3D construct differentiated into target adipose tissue after three days of treatment with insulin, dexamethasone, and IBMX but no EGF; (o) immunostaining of two-dimensional (2D) cultured ASCs with mAbs for CD31+ endothelial cells in green and PI for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red after three days of culture with EGF added in the culture medium; (p) immunostaining of 2D cultured ASCs with mAbs for CD31+ endothelial cells in green and PI for cell nuclei (nucleus) in red after three days of culture without EGF added in the culture medium. Images reproduced with permission from [36].