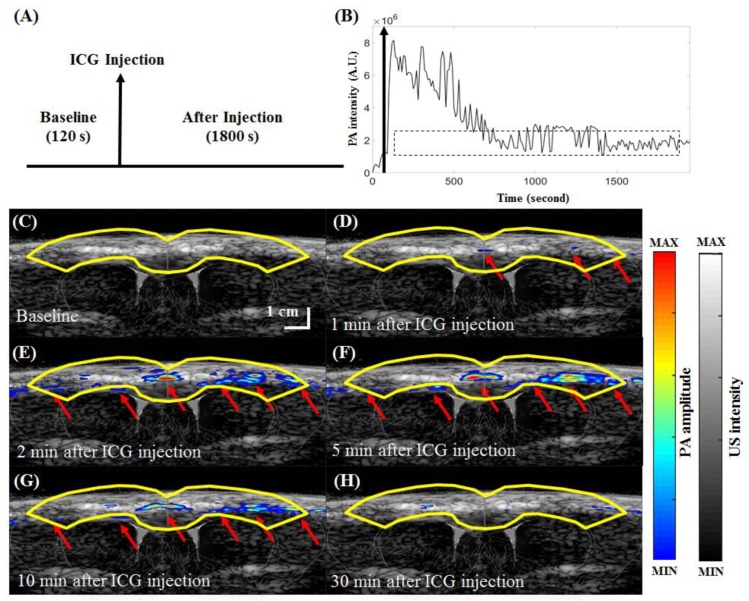
Figure 11.
Real-time visualization of ICG pharmacokinetics acquired by the developed PA system. (A) US/PA data were collected in a block-design paradigm with ICG injection. The task began with 120 s in the baseline state. ICG was injected at the end of the baseline period. After injection, 1800 s of recovery time was monitored. US/PA B-scan imaging began simultaneously with the baseline period and was stopped immediately after the end of the recovery period. The PA B-scan images shown here were acquired at an excitation wavelength of 810 nm. (B) Example plot of the change in PA signal from the cortical region (outlined in solid yellow lines in (C–H)) with time. The baseline intensity at t = 0 was subtracted from all PA signals. ICG injection is indicated by the black arrow. Representative time frames of the baseline-subtracted US/PA overlaid B-scan images of the ROI in yellow at the time points of 5 min before and 1, 2, 5, 10 and 30 min after injection are shown in (C–H), respectively. Images were also combined into a video to illustrate the pharmacokinetics of ICG in real time (Movie S2). The PA images of the ICG-dyed brain acquired at the time points of 1, 2, 5 and 10 min after injection show that ICG accumulation enhanced the PA signal, as indicated by the red arrows, in the cortical region (yellow lines). ICG, indocyanine green; PA, photoacoustic; US, ultrasound; ROI, region of interest.