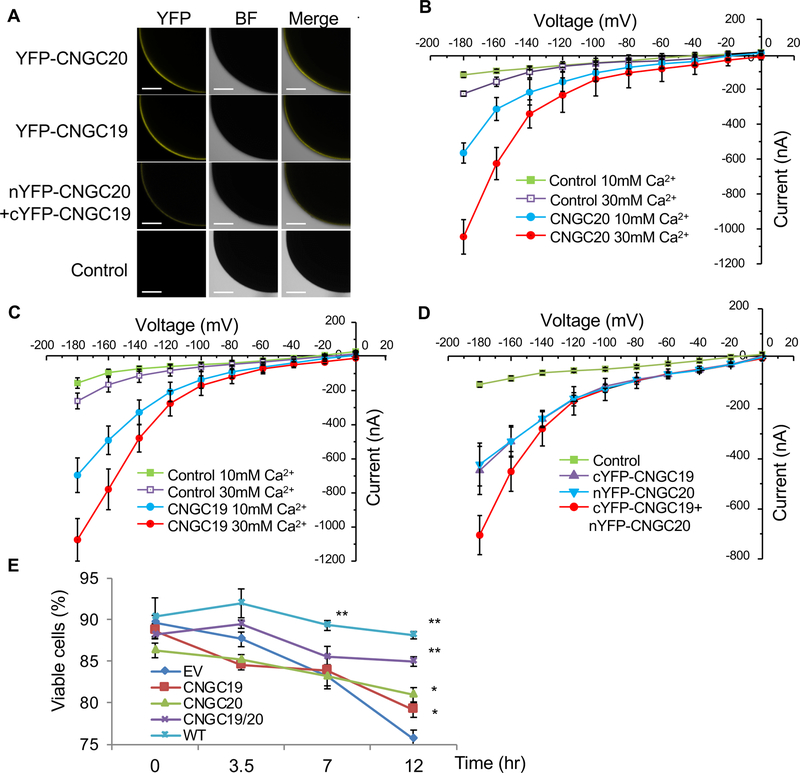
Figure 6. CNGC20 and CNGC19 are Ca2+-permeable channels.
(A) Confocal fluorescence images of oocytes expressing YFP-CNGC20, YFP-CNGC19 or co-expressing nYFP-CNGC20 (N-terminal YFP fused with CNGC20) and cYFP-CNGC19 (C-terminal YFP fused with CNGC19). Water-injected control is showed on the bottom. YFP signals were observed using a confocal microscopy. BF indicates bright field. Bar=200 μm.
(B) CNGC20 exhibits Ca2+-permeable channel activity in Xenopus oocyte. Current-voltage relationship was recorded in oocytes expressing YFP-CNGC20 in the presence of CaCl2. Voltage steps of 0 to −180 mV in 20 mV decrements. Data shown are means ± SE, Control in 10 mM CaCl2 (n = 8) or 30 mM CaCl2 (n=5), CNGC20 in 10 mM CaCl2 (n = 8) or 30 mM CaCl2 (n = 8).
(C) CNGC19 exhibits Ca2+-permeable channel activity when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Current-voltage relationship was recorded in oocytes expressing YFP-CNGC19 in the presence of CaCl2. Voltage steps of 0 to −180 mV in 20 mV decrements. Data shown are means ± SE, Control in 10 mM CaCl2 (n = 10) or 30 mM CaCl2 (n=8), CNGC19 in 10 mM CaCl2 (n=15) or 30 mM CaCl2 (n = 9).
(D) CNGC19 and CNGC20 additively enhance channel activity in Xenopus oocyte. Current-voltage relationship was recorded in oocytes injected with water control (n=6), cYFP-CNGC19 (n=7), nYFP-CNGC20 (n=7), or cYFP-CNGC19+nYFP-CNGC20 (n=12) in the presence of 10 mM CaCl2.
(E) Enhanced Ca2+-permeable channel activity of CNGC19/CNGC20 in yeast complementation analysis. CNGC19/CNGC20 complemented the Ca2+-uptake deficient mutant K927 (cchl::TRP1). Time course after addition of 20 μM α-mating factor is shown. Each data point is average of three independent samples (=independent yeast transformation colony). 200 cells were scored and the percentage of viable cells was calculated.
The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.