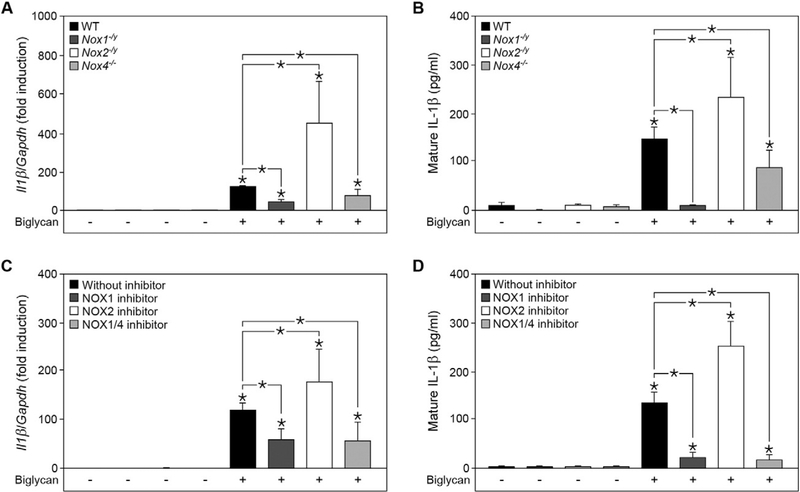
Fig. 2.
Biglycan-induced IL-1β production in macrophages is differentially regulated by NOX1/4 and NOX2. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR for II1β mRNA expression in macrophages isolated from wild-type (WT), Nox1−/y, Nox2−/y and Nox4−/− mice before and after stimulation with biglycan for 6 h (4 μg/ml). (B) ELISA for mature IL-1β in cell culture media from macrophages isolated from WT, Nox1−/y, Nox2−/y and Nox4−/− mice before and after stimulation with biglycan for 16 h. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for II1β mRNA expression in WT macrophages after 1 h pre-incubation with NOX1 inhibitor ML-171 (10 nM), NOX2 inhibitor Nox2ds-tat (40 μM) or NOX1/4 inhibitor GKT137831 (200 μM), with or without biglycan treatment for 6 h; scrambled Nox2ds-tat peptide (40 μM) was used as respective control. (A, C) mRNA expression was normalized to Gapdh and is given as fold induction compared to untreated or scrambled Nox2ds-tat WT controls. (D) ELISA for mature IL-1β in cell culture media of WT macrophages pre-treated with the inhibitors ML-171 (10 nM), Nox2ds-tat (40 μM) or GKT137831 (200 μM), with or without biglycan treatment for 16 h. (A–D) n = 5; data are given as means ± S.D.; *P < 0.05.