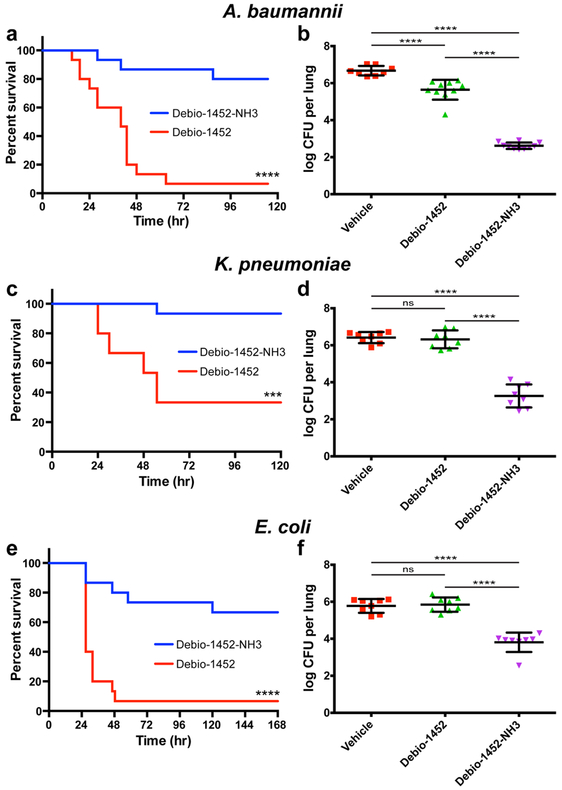
Fig. 3. In vivo efficacy of Debio-1452-NH3.
a. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mouse efficacy model of A. baumannii sepsis. Seven-week old CD-1 mice were infected with A. baumannii W41979 (MIC = 4 μg/mL with Debio-1452-NH3) (2.6x108 CFU/mouse, 15 mice per group) via IV injection. Mice were treated once-a-day for 4 days with FabI inhibitor (IV, 50 mg/kg). Log-rank test, p < 0.0001. b. Acute pneumonia infections initiated in CD-1 mice with A. baumannii W41979 (2.1x108 CFU/mouse, intranasal) were treated with vehicle (8 mice) or FabI inhibitor (10 mice per group) 8, 30, and 48 h post-infection (IV, 50 mg/kg), and the bacterial burden was evaluated 72 h post-infection. c. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of in vivo efficacy model of K. pneumoniae sepsis. Seven-week old CD-1 mice were infected with K. pneumoniae BAA-1705 (MIC = 8 μg/mL with Debio-1452-NH3) (1.08x108 CFU/mouse, 15 mice per group) via IV injection. Mice were treated once-a-day for 4 days with FabI inhibitor (IV, 50 mg/kg). Log-rank test, p < 0.0001. d. K. pneumoniae bacterial burden study. Acute pneumonia infections initiated in CD-1 mice with K. pneumoniae BAA-1705 (4.4x108 CFU/mouse, intranasal) were treated with vehicle or FabI inhibitor (8 mice per group) 6, 23, and 45 h post-infection (IV, 50 mg/kg), and the bacterial burden was evaluated 72 h post-infection. e. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of in vivo efficacy model of E. coli sepsis. Seven-week old CD-1 mice were infected with E. coli AR-0493 (MIC = 4 μg/mL with Debio-1452-NH3) (1.6x108 CFU/mouse, 15 mice per group) via IV injection. Mice were treated once-a-day for 4 days with FabI inhibitor (IV, 50 mg/kg). Log-rank test, p < 0.001. f. E. coli bacterial burden study. Acute pneumonia infections initiated in CD-1 mice with E. coli AR-0493 (1.73x108 CFU/mouse, intranasal) were treated with vehicle or FabI inhibitor (8 mice per group) 6 and 28 h post-infection (IV, 50 mg/kg), and the bacterial burden was evaluated 48 h post-infection. Drugs were formulated in 20% sulfobutyl ether(7) β-cyclodextrin from solid immediately before treatment. For the Kaplan-Meier survival curves (a, c, e), the two-tailed log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to compare survival curves. For the bacterial burden studies (b,d,f), data are shown as mean with error bars representing standard deviation of the mean. For the bacterial burden studies, significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Statistical significance is indicated with asterisks (ns, not significant when p > 0.05 (d, p = 0.9732; f, p = 0.9843), *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001).