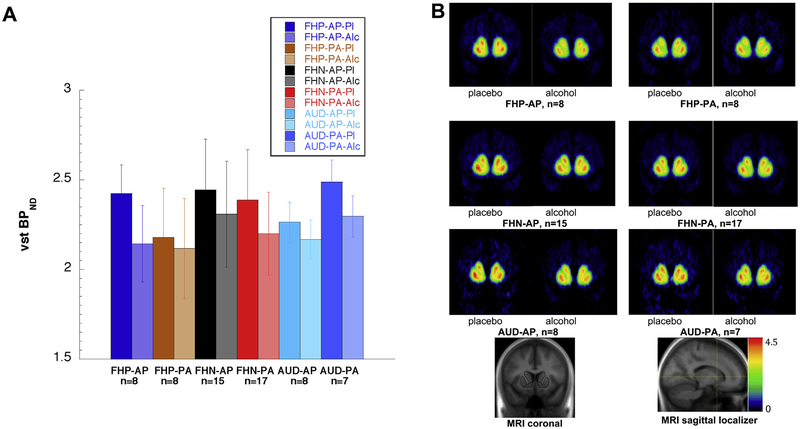
Figure 2.
(A) [11C]Raclopride binding potential (BPND) for each group and drink order. Each group (family history–positive [FHP], family history–negative [FHN], alcohol use disorder [AUD]) is represented by four bars: the placebo day (Pl) and the alcohol day (Alc) for each order (alcohol beverage at first scan [AP]; alcohol beverage at second scan [PA]). In all three groups, alcohol (second bar in each pair) resulted in greater dopamine release (reduction in BPND) than placebo did. However, the FHP participants showed much smaller alcohol-induced reduction in BPND when placebo was first (FHP-PA) than when placebo was second (FHP-AP). In contrast, the FHN and AUD participants showed moderate BPND reductions between placebo and alcohol day that were similar regardless of drink order. The six within-group differences between the placebo and alcohol day for each order (as percent of placebo) are the six data points in Figure 1. Bar heights indicate group mean BPND and error bars indicate SD (data shown in Table 3). (B) [11C]Raclopride BPND for each group and drink order, voxelwise maps. These images display the BPND values shown as regional means in panel (A). Note that the greatest intensity changes from placebo to alcohol scan occur for the FHP-AP group, and the smallest changes occur for the FHP-PA group. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; VST, ventral striatum.