Figure 1.
Expression from Trans-amplifying RNA in Conjunction with nrRNA-Delivered Replicase Activity Is as Efficient as Expression from Self-Amplifying RNA
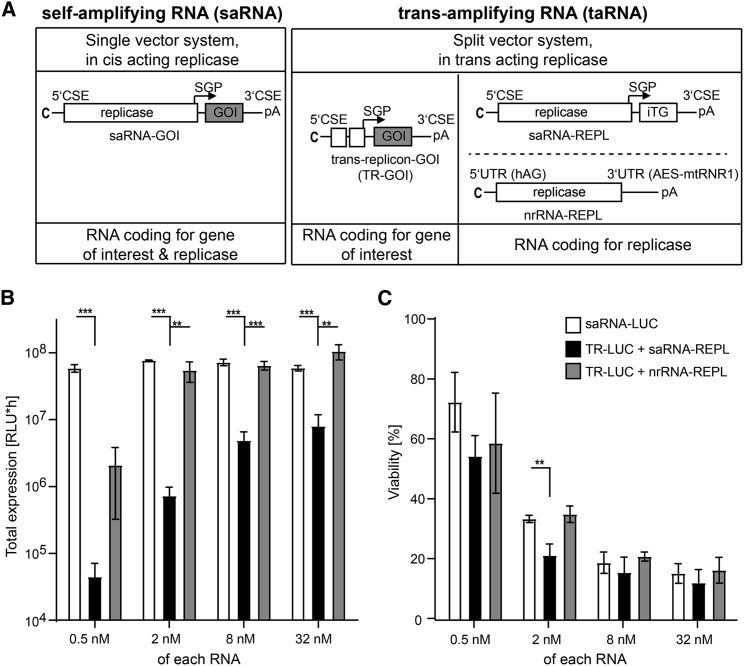
(A) RNA vaccine platforms in this study. Self-amplifying RNA (saRNA, left) is a single-vector system encoding replicase that acts in cis to amplify the complete saRNA, and a second open reading frame with a gene of interest (GOI). Trans-amplifying RNA system (taRNA, right) is a split-vector system consisting of a transreplicon (TR), which encodes the GOI only, and a second RNA delivering alphaviral replicase. TR-GOI is amplified in trans by a replicase either encoded on saRNA (saRNA-REPL) bearing an irrelevant transgene (iTG) or on non-replicative mRNA (nrRNA-REPL). RNA structural elements for replication of saRNA or TRs are located in conserved sequence elements (CSE) at the 5′ and 3′ ends and in the subgenomic promotor (SGP) upstream of the GOI. The UTRs (5′-human alpha globin UTR [hAG] and 3′-AES/mtRNR1-UTR) in the nrRNA-REPL lack viral CSE function and therefore do not promote replication by replicase. All RNAs are capped (C) and bear poly(A) tails (pA). (B) Expression capacity and (C) cytotoxicity of saRNA and taRNA in BHK-21 cells. Vectors bearing firefly luciferase (LUC) as GOI were electroporated into BHK-21 cells (3 × 106 cells per sample) in equimolar amounts. (B) Total luciferase expression was measured for 72 h and approximated by calculating the area under the curve (AUC) for each sample. (C) Relative viability of cells was assessed by measuring viability after 48 h and normalization to the mock control. Mean and SD of three independent experiments are shown. Unpaired Student’s t test was performed (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; not annotated p > 0.05). Raw datasets used for calculating the AUC of the expression time course, as well as the full viability time course, are provided in Figure S1.