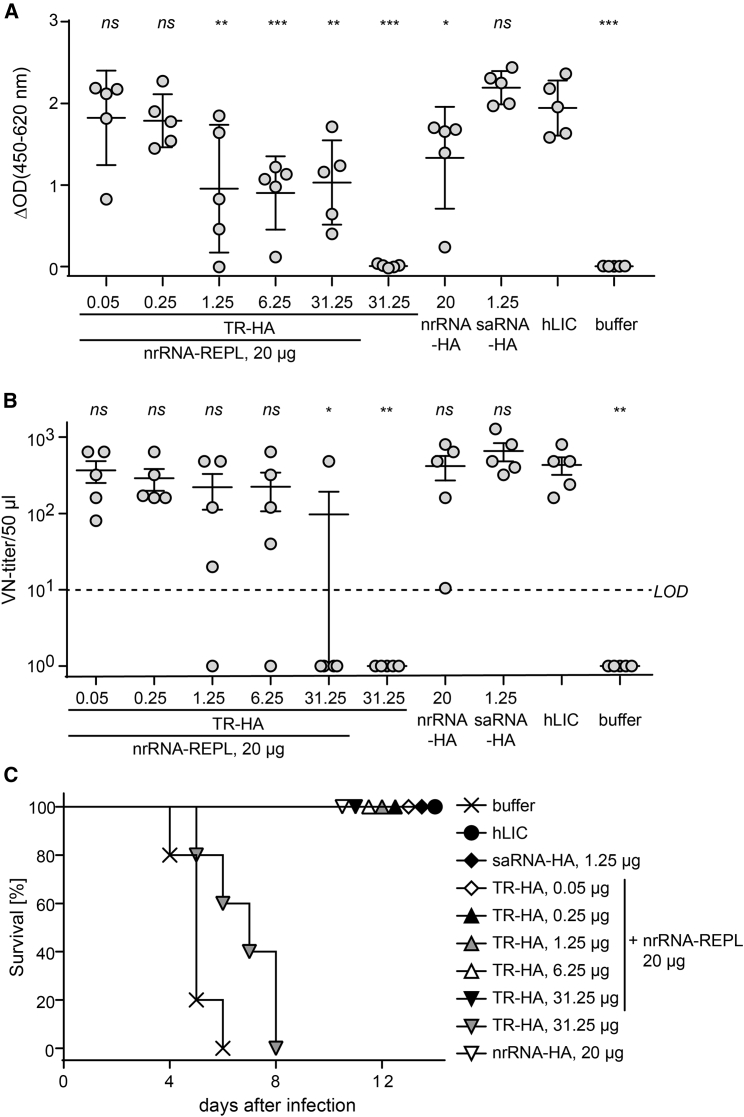
Figure 3.
Immunization with Influenza HA-Encoding taRNA Profoundly Reduces the Doses Required for Inducing Protective Immune Responses in Mice
(A–C) Immune response to influenza HA assessed by (A) ELISA measuring total anti-HA IgG antibody amount, (B) virus neutralization test (VNT), and (C) survival of animals after challenge infections. BALB/c mice were immunized by intradermal injection of varying amounts of TR encoding the hemagglutinin antigen of influenza virus A/California/07/2009(H1N1) (TR-HA) in conjunction with 20 μg nrRNA-REPL. Reference groups received either 20 μg nrRNA-HA or 1.25 μg saRNA-HA. Negative controls received 20 μL buffer without RNA or the highest amount of TR-HA without nrRNA-REPL. Intramuscular injection of 2.4 HA units from human licensed vaccine (hLIC) served as a positive control. Animals were immunized twice at days 0 and 21. Serum for VNT and ELISA was sampled on study day 55 to perform serological analysis. Challenge infection with 10-fold MLD50 of viable influenza A/California/4/2009 (H1N1) was done on study day 56. (A and B) Data are shown as mean and SD of the groups (n = 5). One-way ANOVA was used to calculate statistical significance of difference to the hLIC vaccination (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns p > 0.05). Dashed line in (B) indicates the limit of detection [LOD] of the VNT.) Further data are provided in Figure S3.