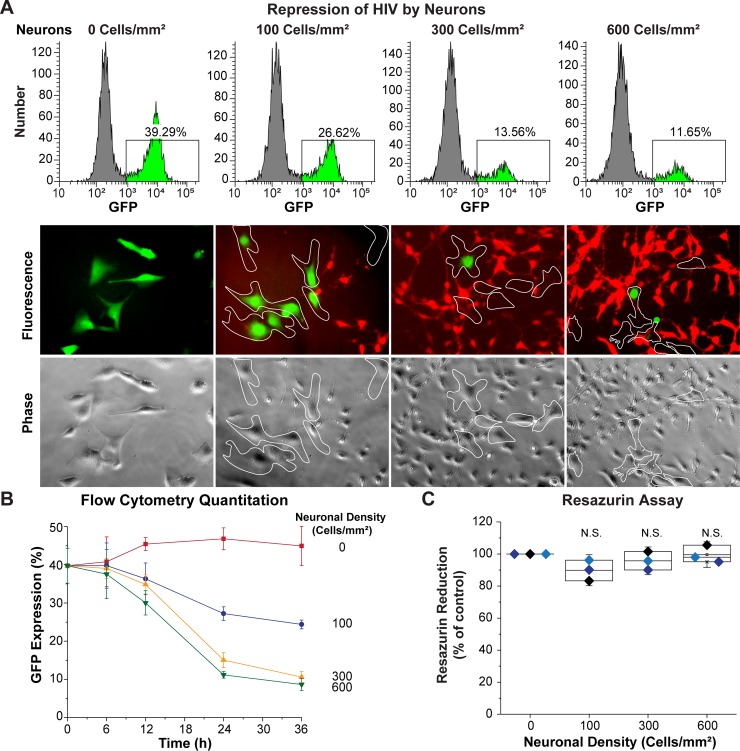
Fig 2. LUHMES-derived neurons inhibit HIV expression.
60,000 HC69 (hμglia/HIV) cells were plated in the absence or presence of increasing densities of LUHMES-derived neurons (Cells/mm2). The level of HIV expression was evaluated after 24 h by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. (A) Flow cytometry profiles from representative single cultures (top) and microscopy (bottom). In the histograms GFP+ cells are indicated in bright green. Microglia were identified by phase contrast microscopy and are outlined by the white contours on the micrographs. (B) Progressive inhibition of HIV expression (Y-axis) at increasing neuronal densities during a time-course of 36 h (X-axis). The error bars represent the SD of n = 3 independent experiments. (C) Resazurin assay to evaluate neuronal viability. The resazurin reduction values (Y-axis) were normalized to the control culture of neurons alone. Each colored symbol represents one experiment. There was no statistically significant (N.S.) differences in cell viability in these experiments.