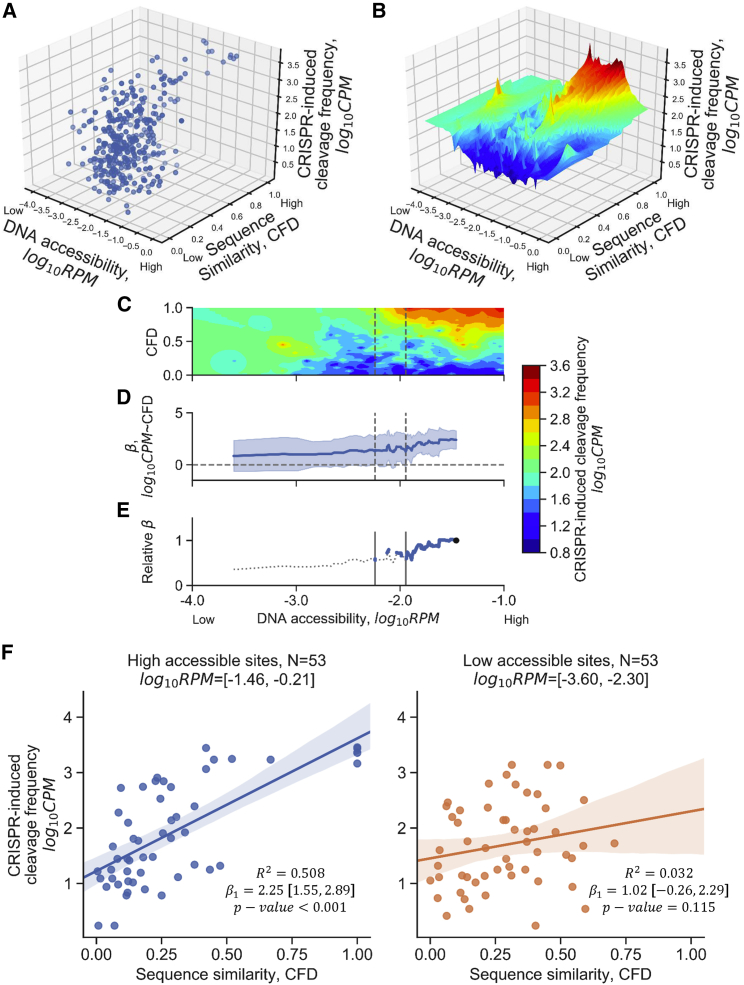
Figure 3.
Low DNA Accessibility Abrogated the Correlation between gRNA:Target Sequence Similarity and CRISPR-Induced Cleavage Frequency
CFD score, RPM, and CPM of cleavage sites in the GS and CS subset (N = 355) were used in this analysis. (A) The three-dimensional scatterplot of sequence similarity, DNA accessibility, and CRISPR-induced cleavage frequency using the CRISPR-induced cleavage sites listed in the GS and CS subset. Each dot represents a CRISPR-induced cleavage site identified by both GUIDE-seq and CIRCLE-seq. CPM represents the number of cleavage events at a CRISPR-induced cleavage site detected by GUIDE-seq; sequence similarity represents the likelihood of CRISPR cutting based on the sequence between gRNA and target using CFD matrix; RPM represents the DNA accessibility at a CRISPR-induced cleavage site. (B) The surface plot estimated by the nearest-neighbor method described in the Materials and Methods. The sequence similarity is estimated by the position-specific matrix of CFD score [0,1] that describes the cleavage possibility of gRNA:target pair at the detected sites. Red represents high cleavage frequency, whereas blue represents low cleavage frequency identified by the GUIDE-seq technique. (C) Contour map of CRISPR-induced cleavage frequency based on the grids of CFD score and DNase-seq RPM; a top-down view of (B). (D) The beta coefficient between CFD and CRISPR-induced cleavage frequency at given 15% quantile of DNA accessibility. Note that the data point was the lower boundary of a given quantile. The shaded regions represent 95% confidence intervals of the t test. The horizontal dashed line at beta coefficient equal to 0 represents the threshold of the significance of the beta coefficient. The correlation was not significant when the 95% confidence interval covered the horizontal line. (E) The beta coefficient relative to the first quantile that contained the cleavage sites with the top 15% DNA accessibility in the GS and CS subset. The dashed line represents the regions that were not significant in the Wald test (D). The right vertical lines represent the threshold of DNA accessibility that started to affect the significance between CFD and CRISPR-induced cleavage frequency. The left vertical line represents the threshold such that the correlation between homology and CRISPR-induced cleavage efficiency was insignificant anywhere below the DNA accessibility. (F) Correlation between CRISPR-induced cleavage frequency and CFD score of the 15% most accessible sites (left panel) or 15% least accessible sites (right panel) in the GS and CS subset. p value of Wald test for a hypothesis test that the slope is 0. β1, beta coefficient of simple linear regression.