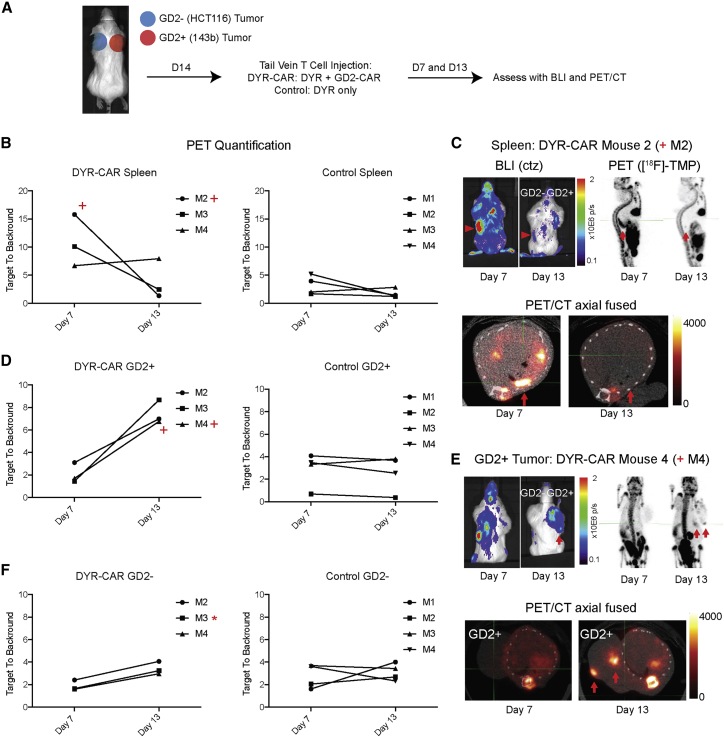
Figure 4.
In Vivo CAR T Cell Trafficking
(A) NSG immunodeficient mice were xenografted in the subcutaneous shoulder regions with GD2+ tumors (143b human osteosarcoma, right shoulder) and GD2− tumors (HCT116 human colon cancer cells, left shoulder), 10 million cells per tumor. The tumors were grown for 14 days when mice were injected with 1 × 106 DYR-CAR T cells or control DYR T cells via tail vein. The mice were imaged on days 7 and 13, first with BLI after coelenterazine (ctz) injection via tail vein and then with PET/CT after [18F]-TMP injection (∼100 μCi via tail vein). For quantification, regions of interest were drawn around the entire tumors, and the signal maximum in the tumors was divided by the signal maximum from the heart/mediastinal blood pool signal, thereby yielding a target-to-background ratio. (B) [18F]-TMP target-to-background ratio in the spleen was increased on day 7 in several mice treated with DYR-CAR T cells, which decreased by day 13. Mice treated with control DYR T cells showed no significant splenic signal over background. (C) Mouse 2 (M2, plus sign) demonstrated BLI and PET signal from the spleen at day 7 that decreased by day 13 (red arrowheads and red arrows). (D) Quantification of PET signal over background at the site of GD2+ 143b tumor at days 7 and 13 in the mice receiving DYR-CAR T cells (left panel) and mice receiving DYR control T cells (right panel). (E) BLI of mouse 4 (M4, plus sign), showing T cells present in the spleen at day 7 and then concentrated at the site GD2+ tumor on day 13. Focal areas of PET signal in the GD2+ tumor on PET/CT images are highlighted with red arrows. (F) Quantification of PET signal over background at the site of GD2− HCT116 tumor at days 7 and 13 in the mice receiving DYR-CAR T cells (left panel) and mice receiving DYR control T cells (right panel). Neither DYR-CAR nor DYR control T cells showed focal areas of [18F]-TMP uptake on PET/CT in HCT116 tumors. However, DYR-CAR mouse 3 (M3, asterisk) did show some signal above background on ex vivo [18F]-TMP autoradiography, which was supported by anti-human CD8 IHC (see Figure S6).