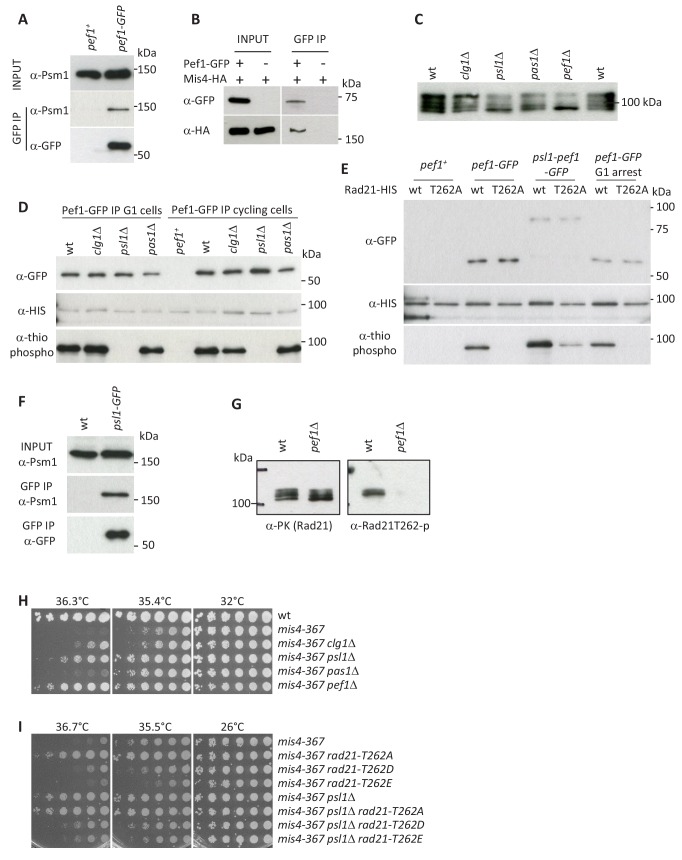
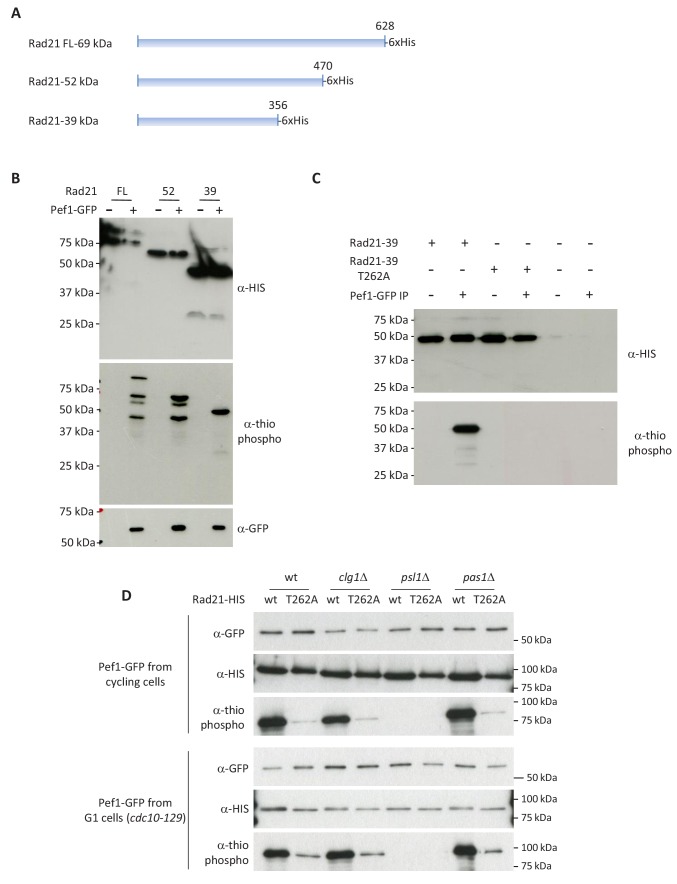
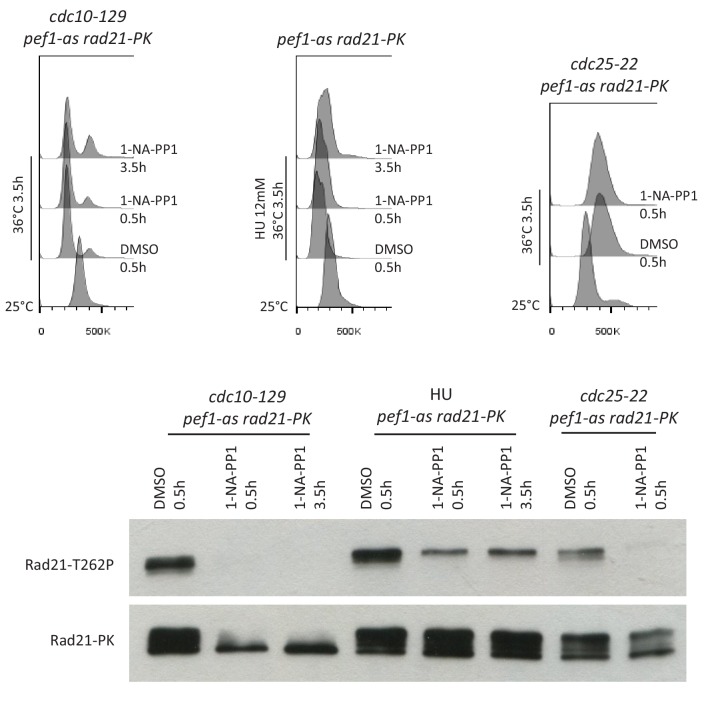
Figure 5. Pef1 phosphorylates Rad21.
(A,B) Pef1 co-immunoprecipitates cohesin (A) and the cohesin loader Mis4 (B) from total protein extracts. (C) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from cycling cells probed with anti-Rad21 antibodies. (D) In vitro kinase assays. Pef1-GFP immuno-purified (IP) from cycling or G1 (cdc10-129) cells was incubated with in vitro translated Rad21-HIS in the presence of ATPγS and the proteins analyzed by western blotting. Phosphorylated products were detected using an anti-thiophosphate ester antibody. (E) In vitro kinase assays. Rad21-T262A prevents Rad21 phosphorylation by Pef1. The fusion protein Psl1-Pef1-GFP phosphorylates Rad21. (F) Psl1 co-immunoprecipitates Psm1 from total protein extracts (cycling cells). (G) Rad21-PK was immuno-purified from cycling cells and probed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (H,I) Growth assays for suppression of the ts growth defect of mis4-367.