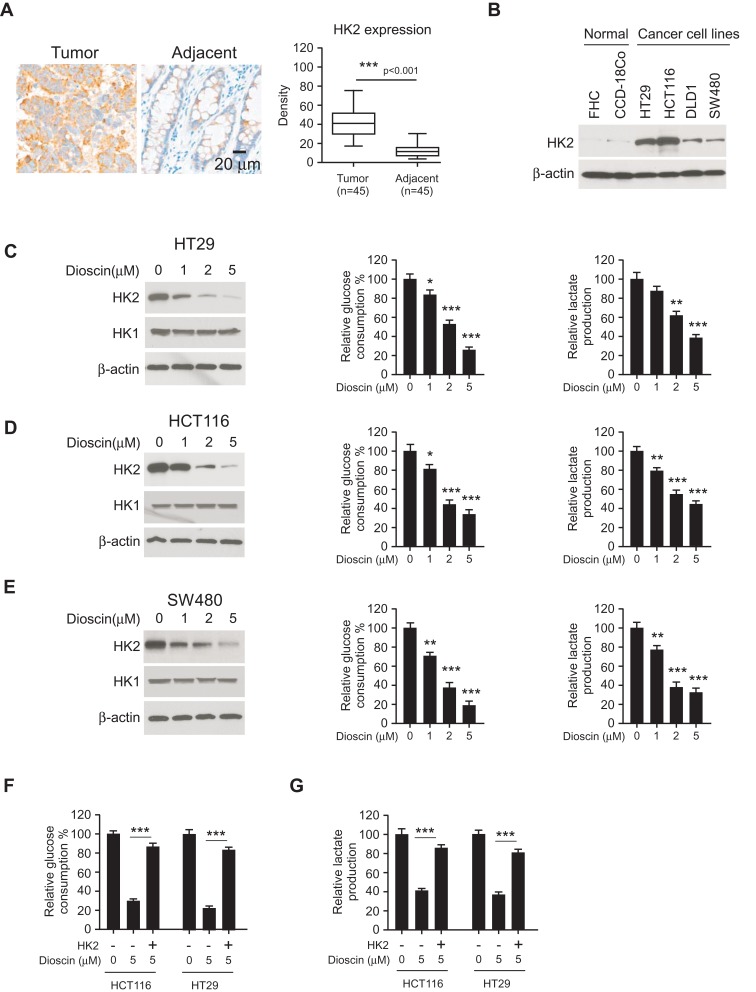
Figure 2.
Dioscin inhibited tumor glycolysis in colorectal cancers by downregulating hexokinase-2. (A) The expression of hexokinase-2 in colorectal cancer tissue and paired adjacent tissue was examined by IHC staining. Left, the representative images; right, the statistics of hexokinase-2 expression. ***p<0.001 indicated a significant difference. (B) The expression of hexokinase-2 in normal colon cells and colorectal cancer cells was examined by Western blotting. (C–E) HT-29 (C), HCT-116 (D) and SW-480 (E) cells were treated with dioscin and the expression of hexokinase-2 (left), glucose consumption (middle) or lactate production (right) was measured, respectively. (F–G) Hexokinase-2 overexpression impaired dioscin-induced glycolysis inhibition. Ectopic overexpression of hexokinase-2 was performed in HCT-116 and HT-29 cells and then treated with 5 μM dioscin, the amount of glucose (F) and lactate (G) were measured as described. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 versus the control.