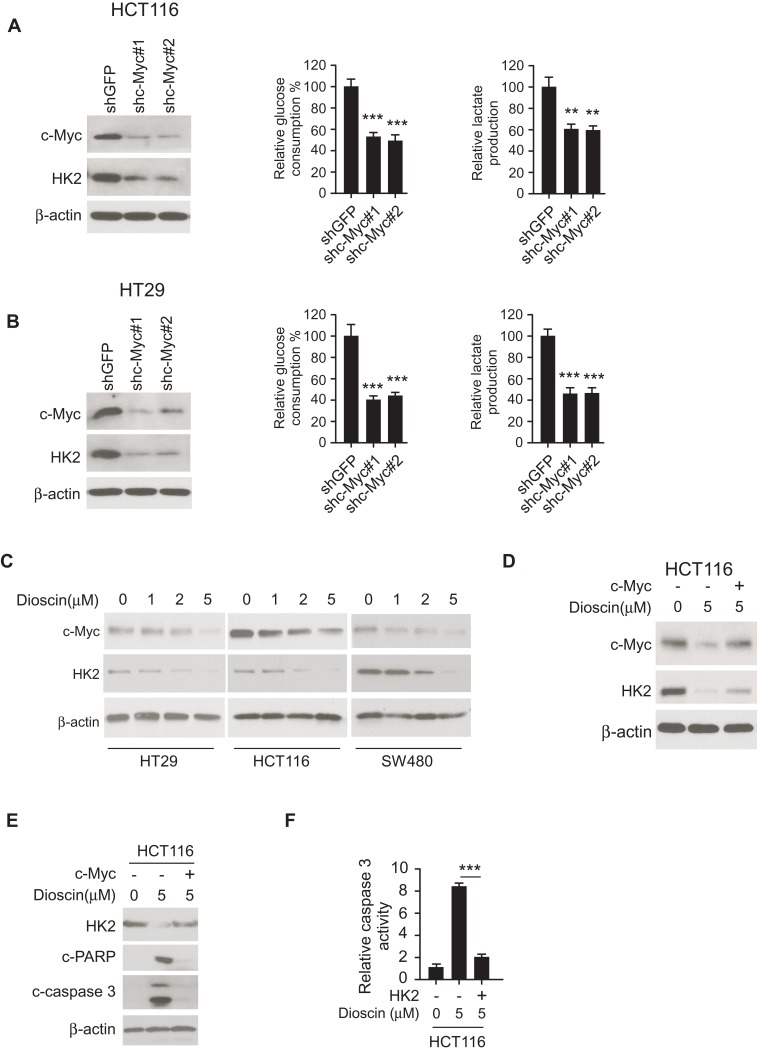
Figure 4.
Dioscin inhibited hexokinase-2 expression by downregulating c-myc. (A, B) c-myc knockdown suppressed hexokinase-2 expression and tumor glycolysis. HCT-116 (A) or HT-29 (B) cells were transfected with c-myc shRNA, the expression of hexokinase-2 in transfected cells (left), glucose consumption (middle) or lactate production (right) was examined. (C) Dioscin reduced c-myc expression in CRC cells. CRC cells were treated with indicated concentrations of dioscin, and the expression of c-myc was detected. (D) Exogenous overexpression of c-myc attenuated hexokinase-2 suppression by dioscin. HCT-116 cells were transfected with plasmids overexpressing c-myc and then treated with 5μM dioscin, the expression of c-myc and hexokinase-2 was detected. (E, F) c-myc ectopic overexpression attenuated dioscin-induced cell apoptosis. HCT-116 cells were transfected with plasmid overexpressing c-myc and then treated with 5μM dioscin, and the expression of HK-2, cleaved PARP and caspase-3 (E) or the activity of caspase-3 (F) was measured. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 represented significant differences.