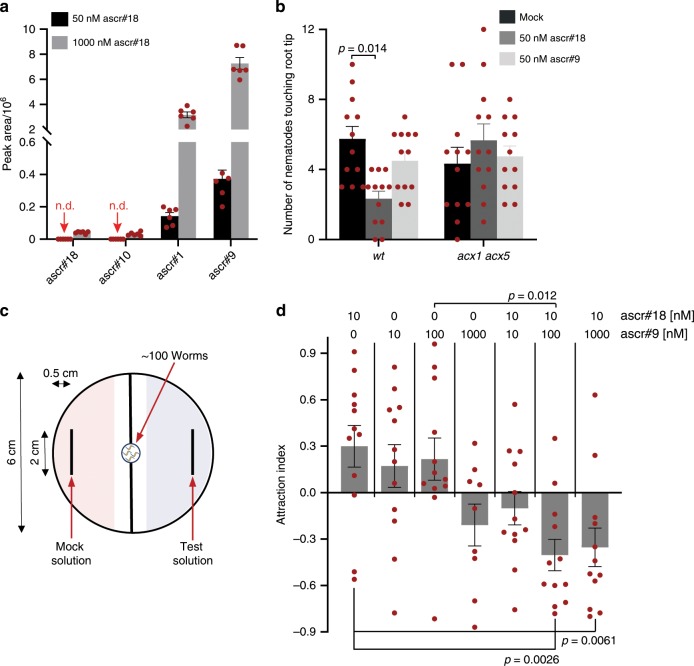
Fig. 5. Plant-derived ascaroside blends deter root-knot nematodes.
a Relative abundances of ascarosides in root exudates of Arabidopsis treated with 50 and 1000 nM ascr#18, as determined LC-MS. Data are average ± SEM (n = 6), n.d. = not detected. b Arabidopsis wildtype and acx1 acx5 were treated with 50 nM ascr#18 or ascr#9 for 48 h before transfer into 12-well plates containing Pluronic F-127 gel with ~200 freshly hatched M. incognita J2 larvae. Larvae touching the terminal part of roots were counted at 6 h after seedling transfer. Data are average ± s.d. (n = 12). c A small volume (10 µL) of ascr#18, ascr#9, or ascr#18/ascr#9 solutions was placed on one side of a 6-cm Petri dish with mock solutions on the other side. Subsequently, ~100 freshly hatched M. incognita J2 larvae were placed in the center of the plate. Larvae in the indicated scoring areas were counted after 4 h. d Attraction index for different concentrations of ascr#18, ascr#9, or ascr#18/ascr#9 mixtures measured using the layout shown in c. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 12). Adjusted p-values in Fig. 5b were calculated by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparisons post hoc test. For Fig. 5d, adjusted p-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparisons post hoc test. Source data are provided as a data file.