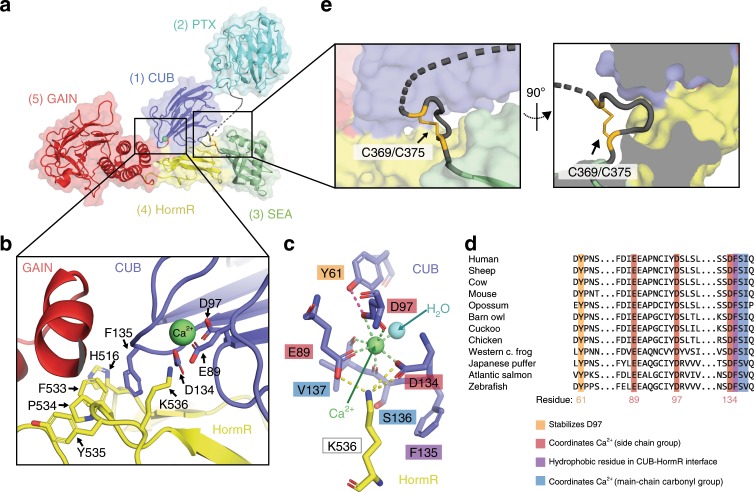
Fig. 2. Closed conformation of Gpr126 is mediated by CUB-HormR-linker interactions.
a Structure of the full ECR of (−ss) Gpr126. b Close-up view of the CUB-HormR interface. Resides at the interface are shown as sticks. The calcium ion is shown as a bright green sphere. c Close-up view of the calcium-coordination site within CUB domain. The water molecule is shown as a blue sphere. The residues are shown as sticks. CUB residues are colored dark blue and HormR residue is colored yellow. Residue labels are colored according to their roles in CUB-HormR interaction: red (E89, D97, D134) represents calcium coordination by side-chain residue, blue (S136, V137) represents calcium coordination by main-chain carbonyl group, purple (F135) represents a hydrophobic residue in CUB-HormR interface, and orange (Y61) represents a residue that stabilizes calcium-coordinating residue D97. Calcium coordination is shown as bright green dashed lines. CUB-HormR interaction is shown as yellow dashed lines. The interaction between Y61 and D97 is shown as a magenta dashed line. d Sequence alignment of partial Gpr126 CUB domain from various species, highlighting important conserved residues: calcium-coordinating residues by side-chain group (red), calcium-coordinating residues by main-chain carbonyl (blue), a tyrosine residue that stabilizes a calcium-coordinating residue (orange), and a hydrophobic phenylalanine residue in the CUB-HormR interface (purple). e Close-up view of the disulfide-stabilized loop inserted between CUB and HormR domains. The disulfide bond is colored bright orange and is indicated by an arrow. The dashed line represents disordered residues in the linker region.