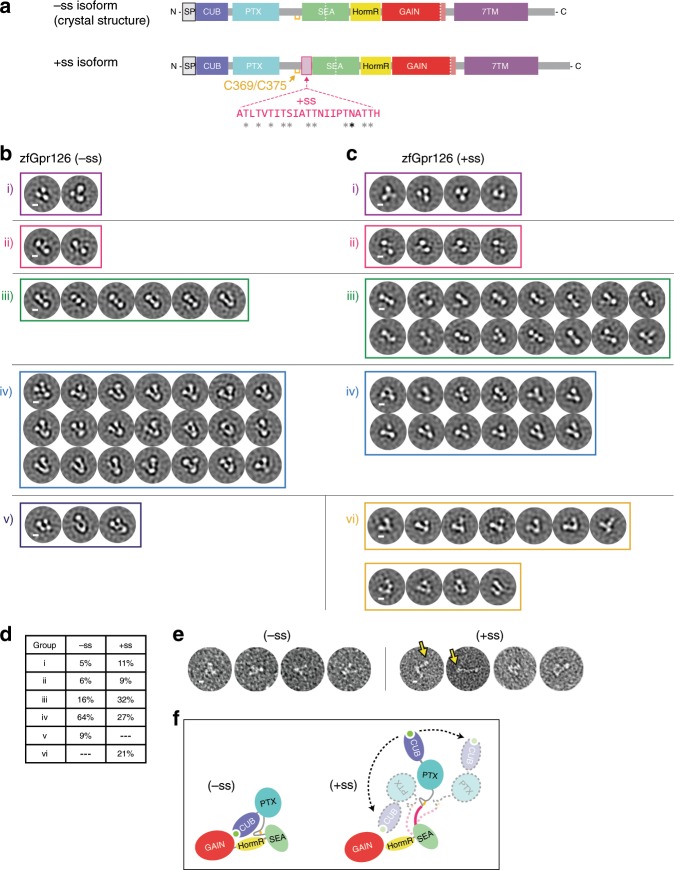
Fig. 3. Alternative splice isoforms of Gpr126 modulate ECR conformation.
a Schematic diagram of Gpr126 splice isoforms generated by including (+ss) or excluding (−ss) exon 6. Residues encoded by exon 6 are colored magenta. Gray asterisks indicate potential O-linked glycosylation sites and the black asterisk indicates a predicted N-linked glycosylation site. The conserved disulfide bond in the linker is colored yellow. b, c Negative-stain EM 2D class averages for −ss (b) and +ss (c) ECR constructs. Class averages are categorized according to similar orientations: (i, ii, iii, iv, v, and vi). (i, ii, iii, iv) are observed in both –ss and +ss isoforms. (vi) represents open-like conformations (>50° angle) that are observed only in the +ss isoform. (v) represents unidentifiable miscellaneous views. Scale bars (white) represent 50 Å. d Quantification of percentage of particles per category for both isoforms. e Representative individual particles for both isoforms. Yellow arrows point to particles which are not in a closed conformation. f ECR conformations based on negative-stain EM are depicted as cartoons. The splice site is shown in magenta. Black arrows with dashed lines indicate dynamic ECR conformation.