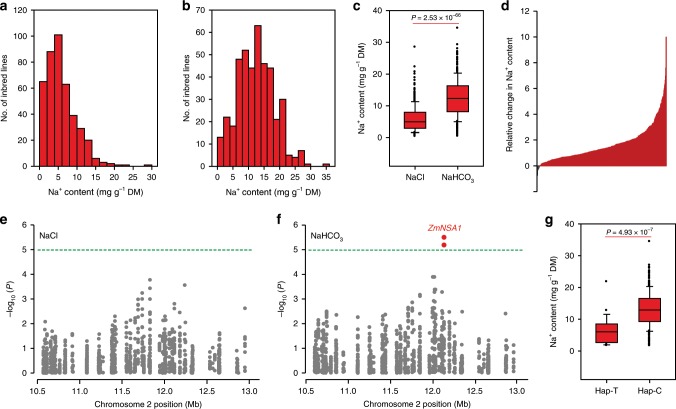
Fig. 1. ZmNSA1 confers natural variations of shoot Na+ contents under NaHCO3 condition.
a, b Distribution of shoot-Na+ contents among 419 maize inbred lines under conditions with 100 mM NaCl (a) or 100 mM NaHCO3 (b). c Comparison of the shoot Na+ contents under NaCl and NaHCO3 conditions. The box shows the median, lower and upper quartiles, and dots denote outliers. Statistical significance was determined by a two-sided t-test (n = 419). d The relative change in shoot Na+ contents under NaHCO3 condition as compared with NaCl condition. The data were expressed as (m − n)/n. m and n referred to the shoot Na+ contents under NaHCO3 and NaCl condition respectively. e, f GWAS results of shoot Na+ contents under NaCl (e) and NaHCO3 (f) condition. A 2.5 Mb region (Chr2: 10.5–13.0 Mb) was displayed. Two SNPs (Chr2_12130275 and Chr2_12130134) that showed significantly association with shoot Na+ content under NaHCO3 condition were highlighted in red, and the gene underlies the association was designated as ZmNSA1 (Na+ Content under Saline-Alkaline Condition). g The distribution of shoot Na+ contents. Statistical significance was determined by a two-sided t-test (n = 375 for genotype C; n = 23 for genotype T). The samples were grouped according to the haplotypes of SNP Chr2_12130275. Source data underlying Fig. 1d, g are provided as a Source Data file.