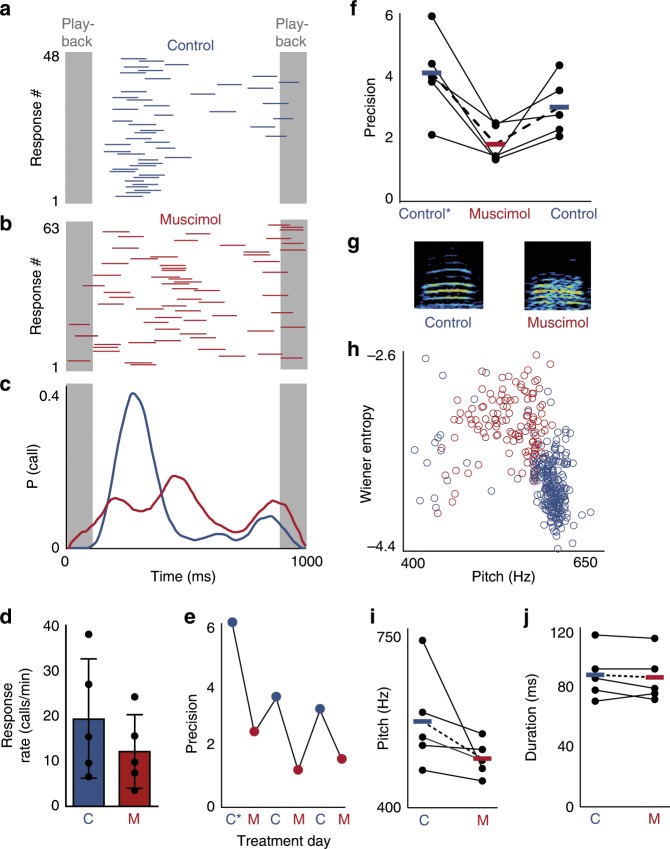
Fig. 2. HVC is required for precise timing of calling behavior.
a Call responses (blue) to call playbacks (gray) for example bird during infusion of saline. b Call responses during bilateral infusion of 5 mM muscimol. c Response probability distributions for control (blue) and muscimol (red) conditions in (a, b). d Average response rate during control and muscimol conditions (control = 19.32 ± 11.66 calls/min, muscimol = 12.12 ± 7.19 calls/min, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p < 0.05, n = 5 birds), error bars: standard deviation. e Effects of HVC inactivation on response latency precision for an example bird across 6 days starting with pre-surgery (C*) and alternating daily between muscimol (M) and saline infusion (C). f Response latency precision assessed pre-surgery (control*), during HVC inactivation (muscimol), and during saline (control) infusion (mean precision: C* = 4.13 ± 1.37, M = 1.83 ± 0.60, C = 3.02 ± 0.95, one-tailed Wilcoxon signed-rank test, C* vs. M: p = 0.031, C vs. M: p = 0.031, n = 5 birds, bars and dotted lines represent means). g Spectrograms of two calls recorded during a control condition (left) and a muscimol infusion (right). h Effects of HVC inactivation on acoustic features of calls for example bird in (g). Wiener Entropy i.e. the noisiness of calls (where white noise would have a value of 0 and a pure tone would have a large negative value) increases when muscimol is applied (red circles, n = 121 calls) whereas the pitch is higher in the saline control condition (blue circles, n = 261 calls). i Median pitch during saline control (blue) and muscimol (red) application (mean pitch ± s.d. for control = 568.5 ± 97.4 Hz, pitch for muscimol = 495.6 ± 35.1 Hz, n = 5 birds. j Duration of calls during control and muscimol conditions (mean duration for control = 89 ± 17 ms, mean duration for muscimol = 87 ± 17 ms, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.3750, n = 5 birds). Source data is available as a Source Data file.