Figure 2.
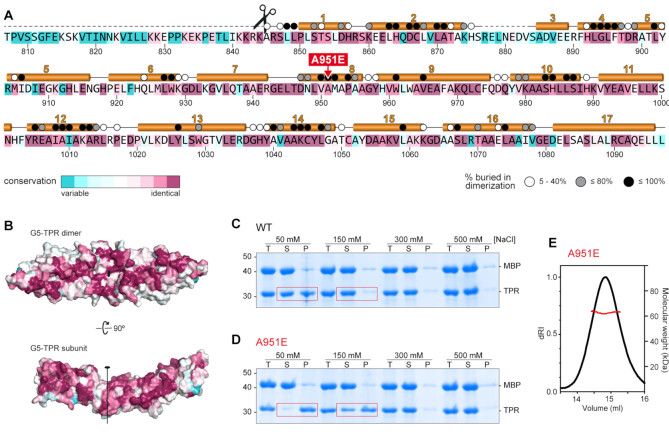
The conserved dimerization module in Gemin5 is destabilized by mutation A951E. (A) Gemin5 TPR-like sequence colored according to the conservation, from magenta (identity) to cyan (variable), based on the alignment of 145 Gemin5 sequences. The α-helices are depicted above the sequence, and missing regions in the model are indicated with dashed lines. The scissors mark the L protease cleavage motif. Residues buried up to 40%, 80% or 100% in the dimerization interface are denoted respectively with a white, grey or black dot on top. The substitution of residue A951 by glutamate is indicated in red. (B) Sequence conservation plotted on the surface of the protein dimer and on the dimerization interface. The molecules are represented in the same orientation as in Figure 1G. (C, D) Solubility of the MBP-cleaved G5-TPR and A951E variant monitored by SDS-PAGE in conditions with different concentrations of NaCl, showing the total (T), soluble (S) and precipitated (P) fractions. Red boxes highlight the decreased solubility of mutant A951E at lower salt concentrations. (E) SEC-MALS analysis proves that under conditions with 0.5 M NaCl, the A951E mutant forms dimers with a molecular weight of 63 kDa (±0.05%).