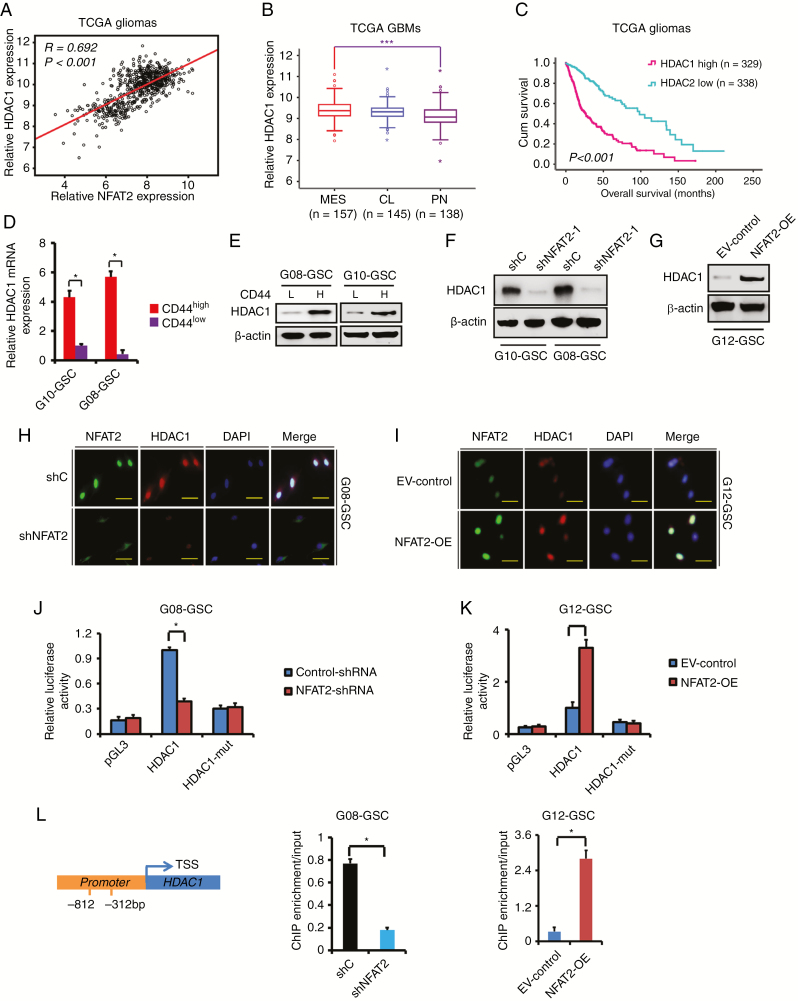
Fig. 5.
NFAT2 regulates the expression of HDAC1 in GSCs. (A) The expression of HDAC1 was significantly correlated with that of NFAT2 in TCGA gliomas. (B) The mRNA expression of HDAC1 is shown according to molecular subtypes of TCGA GBMs. (C) The prognostic significance of HDAC1 is examined in TCGA gliomas. (D, E) The expression of HDAC1 in CD44high and CD44low GSCs was examined by real-time PCR (D) and WB (E). (F) The effect of NFAT2 knockdown on the expression of HDAC1 was examined by western blotting in G08 and G10 GSCs. (G) The effect of NFAT2 overexpression on the expression of HDAC1 was examined by western blotting in G12 GSCs. (H, I) Double-labeled immunofluorescence staining demonstrates that NFAT2-knockdown is accompanied by reduced HDAC1 expression in G08 (H), while NFAT2 overexpression is accompanied by increased HDAC1 expression in G12 (I). Scale bar = 25 μm. (J, K) Effect of NFAT2 on HDAC1 promoter activities. Knockdown of NFAT2 in G08 significantly suppresses the luciferase activity driven by the wildtype HDAC1 promoters compared with control-shRNA. Mutating NFAT2 binding sites markedly decreases promoter activity compared with the wildtype promoter (J). NFAT2 overexpression in G12 enhances luciferase promoter activities (K). (L) Binding of NFAT2 to HDAC1 promoters. Binding of NFAT2 is suppressed when NFAT2 is knocked down in G08, while binding is enhanced when NFAT2 is overexpressed in G12. Results are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate samples from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.