Fig. 1.
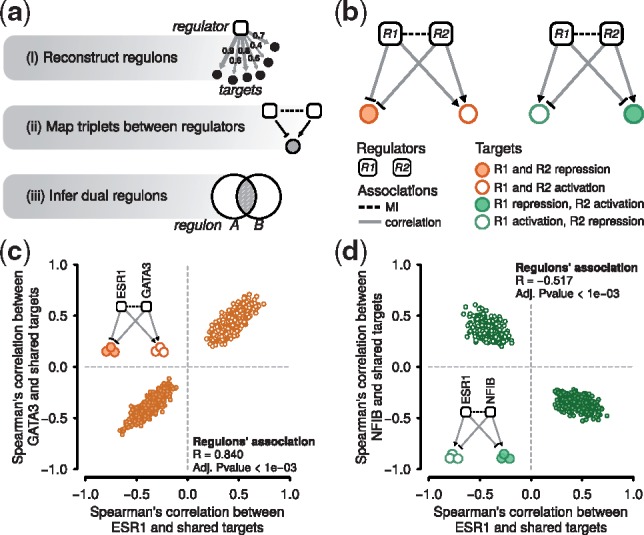
Inference of dual regulons. (a) RTNduals computes dual regulons using: (i) MI between a regulator and targets; (ii) triplets consisting of pairs of regulators and a shared target; (iii) whether the number of shared targets is statistically significant. (b) Examples showing two associated regulators and two regulator-target triples. Left: an example in which the regulators co-operate by influencing shared target genes in the same direction (i.e. either co-activating or co-repressing the shared targets). Right: regulators compete by influencing shared target genes in opposite directions. (c, d) Distribution of correlation coefficients between regulators and shared targets in two example dual regulons, computed from the expression profiles of METABRIC breast cancer data, n = 997 for cohort 1 (Curtis et al., 2012).
