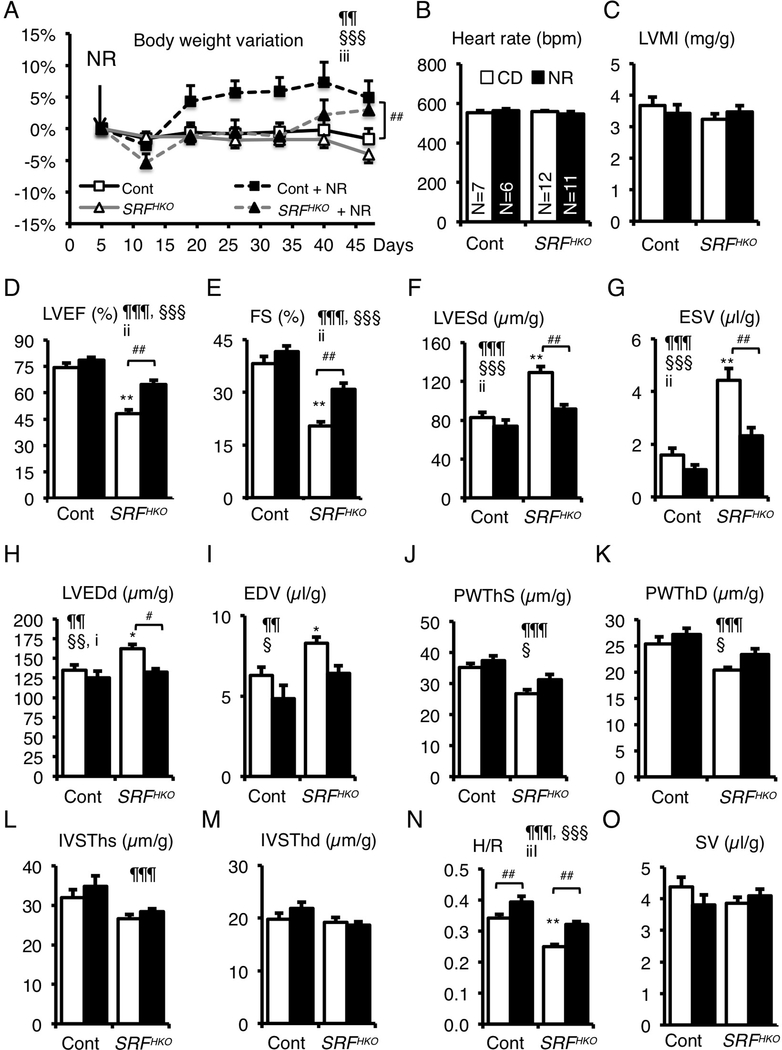
Figure 2. NR supplementation in diet prevents the onset of heart failure and dilatation.
(A) CD or NR supplemented diet (0.22 %) was given ad libitum to control and SRFHKO mice from D5 after SRF inactivation to the end of the experiment. Body weight was monitored throughout the period. Data are expressed as mean % weight variation ± SEM, compared to weight at D5. A Two-Factor ANOVA with repeated measures on one factor was used for statistical analysis. §§§ p≤ 0.001 for the time effect; iii, p≤ 0.001 for the interaction effect. Tukey test: * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 for any time point versus day 5 within a group; #, p≤ 0.05 for the NR treatment in SRFHKO group.
(B-O) Cardiac parameters of control and SRFHKO mutant were analyzed in M-Mode echocardiography between D45 to D47. (B) Heart rate; (C) Left ventricle (LV) mass index; (D) LV ejection fraction; (E) Fractional shortening; (F, G) LV end-systolic diameter (D) and volume (G); (H, I) LV end-diastolic diameter (H) and volume (I); (J, K); LV posterior wall thickness in systole (J) and diastole (K); (L, M) Interventricular septum thickness in systole (L) and diastole (M); (N) H/R: LV thickness (H) to radius (R) ratio; (O) Stroke volume. Dimensions were normalized by the body weight. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis: two-way factorial ANOVA for independent samples. ¶¶ p≤ 0.01, ¶¶¶ p≤ 0.001 for the genotype effect; § p≤ 0.05, §§ p≤ 0.01, §§§ p≤ 0.001 for the NR treatment effect; i p≤0.05, ii p≤ 0.01, iii p≤0.001 for the interaction effect. Tukey test: Asterisks indicate statistical significant difference versus the control CD group: * p≤ 0.05, ** p≤ 0.01, *** p≤ 0.001. # p≤ 0.05, ## p≤ 0.01 for the effect of NR within the SRFHKO group.