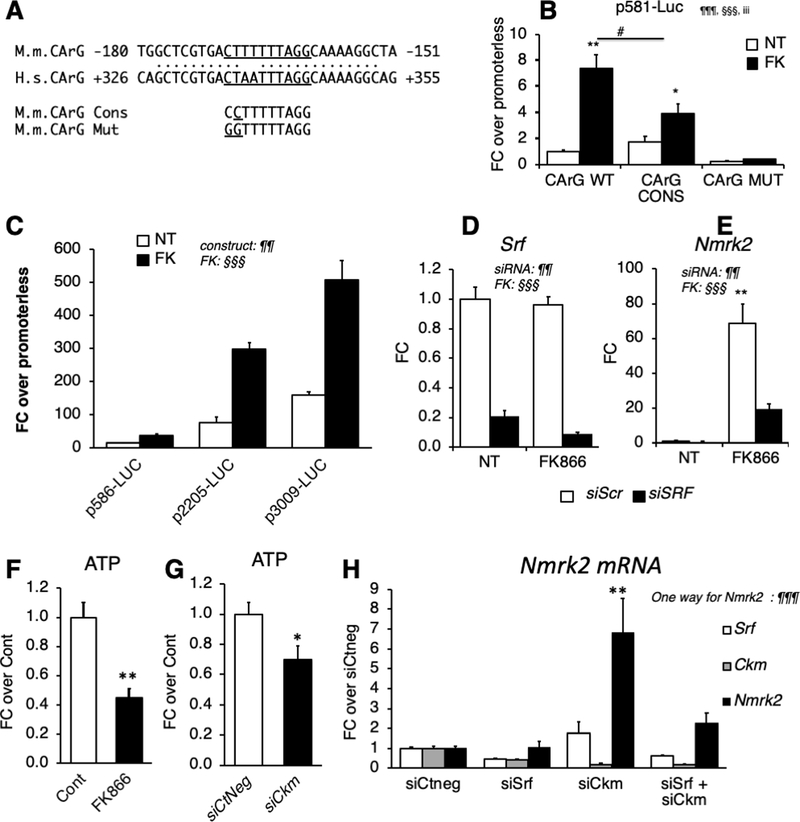
Figure 5. SRF is a component of Nmrk2 gene transcription.
(A) CArG-like binding site for SRF in the conserved region between the murine (M.m) Nmrk2 promoter and human (H.s) NMRK2 intron 1. The CArG-like motif was mutated to a CArG consensus sequence (cons) and a CArG mutant (mut) site unable to bind SRF.
(B) Activity of p586-Firefly Luciferase construct bearing wild-type (WT), consensus (CONS) or mutated (Mut) CArG motif (H) or longer fragments (I), without (NT) or with FK866 treatment (10 μM). SV40-renilla luciferase was co-transfected with the Nmrk2-Firefly Luc constructs for normalization of transfection efficiency.
(C) Various lengths of the murine Nmrk2 regulatory region were inserted into pGL4 vector and transfected in non-treated or FK866 treated cells.
(D, E) Srf and Nmrk2 mRNA levels in NRC transfected with control scrambled siRNA (siScr) or Srf si-RNA, without (NT) or with FK866 treatment.
(F, G) ATP levels in cells treated for 72h with FK866 (F) or siCkm (G).
(H) Srf, Ckm and Nmrk2 mRNA level in NRCs transfected for 72h with siRNAs as indicated.
Throughout the figure, data are expressed as mean ± SEM over control group, Fc, fold change over control group except for panel B and C, fold change over promoterless pGL4 plasmid and H FC over siCtneg. Two-way factorial ANOVA for independent factors was used for panels B to E. ¶ and § symbols as indicated in the panels; iii p≤0.001 for the interaction effect. A T-test was used for panels F and G; * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01,between FK treated cells or siCkm transfected cells versus control cells or siCtneg transfected cells, respectively. A one-way ANOVA was used in panel H. §§§ p≤ 0.001. Post-hoc Tukey test: ** p< 0.01, between any group versus siCtneg transfected control cells.