Figure 1.
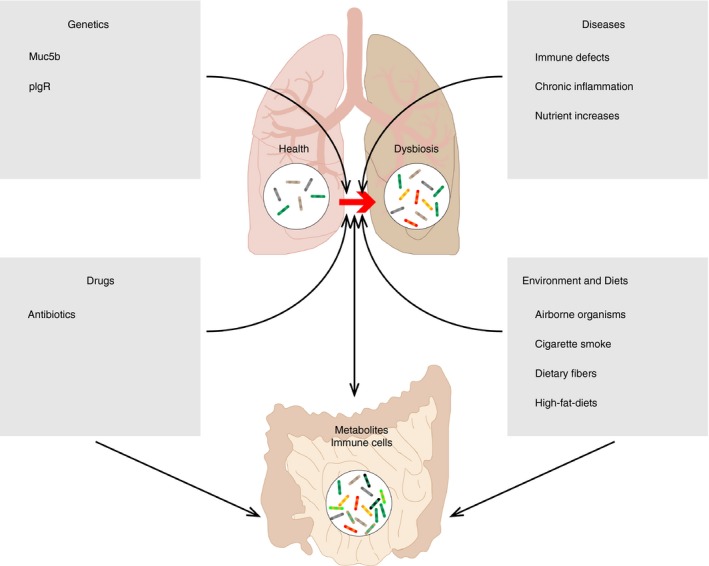
Internal and external factors that lead to lung microbiota dysbiosis. Genetic deficiency of Muc5b or pIgR causes direct barrier disruption in lung; drugs including antibiotics can either target local immune cells to inhibit their activity or target bacteria to prevent their survival; progression of many pulmonary diseases including viral infections and fibrosis is usually accompanied with immune defects, chronic inflammation and nutrient increases; airborne organisms and cigarette smoking may directly or indirectly shift pulmonary bacterial composition while dietary changes are associated with changes of metabolites that have systemic effects on the immune system; the lung may closely interact with the gut to form the lung−gut axis, which is mainly mediated by metabolites changes and status changes of immune cells.
