Figure 2.
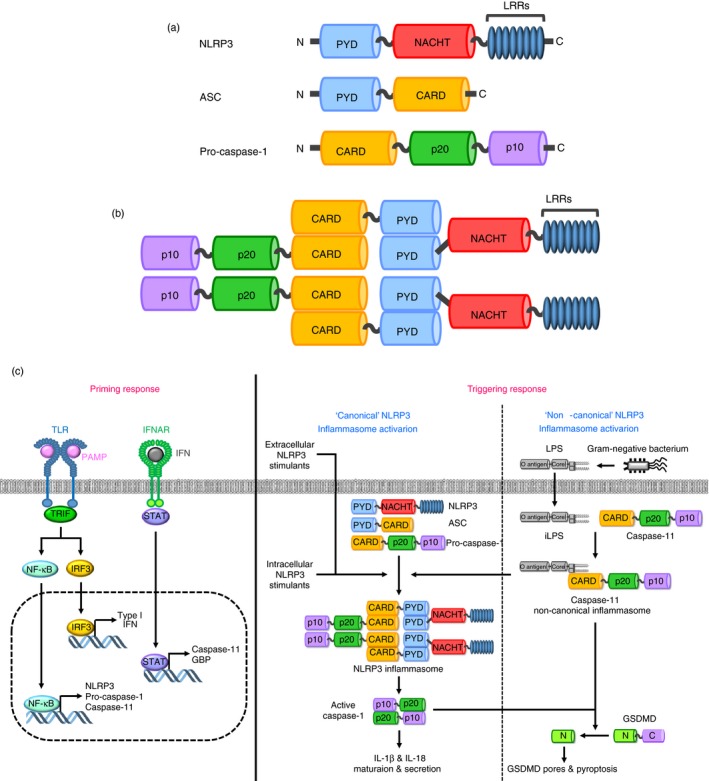
Structure and activation of canonical and non‐canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes (a) Domain structures of NLRP3, ASC and pro‐caspase‐1. NLRP3 consists of three main domains; an N‐terminal PYD, a NACHT and C‐terminal LRRs. ASC consists of two main domains; an N‐terminal PYD and a C‐terminal CARD. Pro‐caspase‐1 consists of three main domains; an N‐terminal CARD, a p20 and a C‐terminal p10. (b) Structure of the NLRP3 inflammasome. NLRP3 binds with ASC via their PYDs, and then pro‐caspase‐1 is recruited and binds with ASC via their CARDs. (c) Two‐signal model for the activation of canonical and non‐canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes. In the priming response, interaction between extracellular PAMPs and PRRs, such as TLRs, induces the transduction cascades of the inflammatory NF‐κB and IRF3 signalling pathways by activating TRIF, resulting in the upregulation of the expression of inflammatory molecules, such as NLRP3, pro‐caspase‐1, caspase‐11 and type I IFN necessary for the subsequent activation of the canonical and non‐canonical NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. The produced type I IFN in turn interacts with extracellular IFNAR in an autocrine manner, and the IFN signalling upregulates the expression of caspase‐11 and GBP. In the triggering response, extracellular and intracellular NLRP3 ligands interact with NLRP3, resulting in canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation. LPS internalized from the Gram‐negative bacteria directly interacts with caspase‐11, leading to caspase‐11 non‐canonical inflammasome activation, and the activated caspase‐11 non‐canonical inflammasome, in turn, induces non‐canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Activation of canonical and non‐canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes activates caspase‐1, and the activated caspase‐1 induces IL‐1β and IL‐18 secretion and GSDMD‐mediated pyroptosis. CARD, caspase recruit domain; GBP, guanylate‐binding protein; GSDMD, gasdermin D; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, type I IFN receptor; IL, interleukin; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; LRRs, leucine‐rich repeats; NACHT, nucleotide‐binding and oligomerization domain; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐kappa B; NLR, NOD‐like receptor; PAMP, pathogen‐associated molecular pattern; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; PYD, pyrin domain; TRIF, TIR‐domain‐containing adapter‐inducing interferon β.
