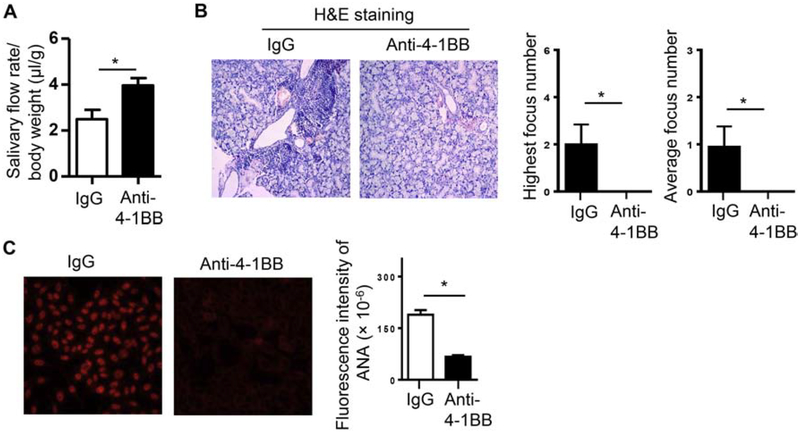
Figure 1. Administration of an agonistic anti-4–1BB antibody impeded the development of SS-like sialadenitis and hyposalivation in female NOD mice.
Anti-4–1BB antibody or isotype IgG was i.p.-administered to 7-week-old female NOD mice 3 times weekly for 2 weeks, and the mice were analyzed for SS pathologies two weeks after the last injection. (A) Stimulated salivary flow rate normalized to body weight. (B) Left panels, images of H&E staining of SMG sections (200X magnification); right panels, statistical analysis of the highest focus number and the average focus number of the 3 non-consecutive SMG sections from each mouse in the control and anti-4–1BB-treated groups. (C) Serum ANA assay. Left panels, images of the immunofluorescence staining of ANA (200X magnification). Right panels, fluorescence intensity of ANA staining. Data are representative or the average of 8 mice per group. Error bars represent the SEM.* p<0.05