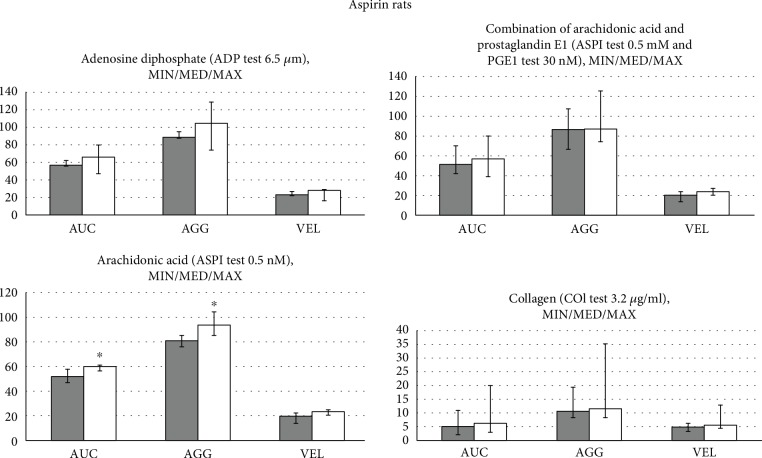
Figure 1.
Rats which underwent antithrombotic agent aspirin (10 mg/kg intragastrically, once daily for three days) received immediately thereafter BPC 157 (10 μg/kg intragastrically, once daily for three days) (white bars) or an equal volume of saline (5 ml/kg, intragastrically, once daily for three days) (gray bars); they were sacrificed at 2 h after the last application. Platelet aggregation was determined in whole blood by multiple electrode aggregometry (MEA) on Multiplate® Analyzer (aggregation (AGG)) (highest increase in impedance between the electrodes measured in aggregation units (AU)), area under the curve (AUC) (determined by the height of the aggregation curve and the slope measured in U = AU/min (1 U = 10 AU/min)), and velocity (VEL) (maximum slope of aggregation measured in AU/minute). After the incubation, 20 μl of the agonist was added to each respective cell: adenosine diphosphate (ADP test 6.5 μM), arachidonic acid (ASPI test 0.5 mM), a combination of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin E1 (ASPI test 0.5 mM and PGE1 test 30 nM), and collagen (COL test 3.2 μg/ml). After six minutes of measurement, AUC, AGG, and VEL were recorded. ∗P < 0.05, vs. control, at least.