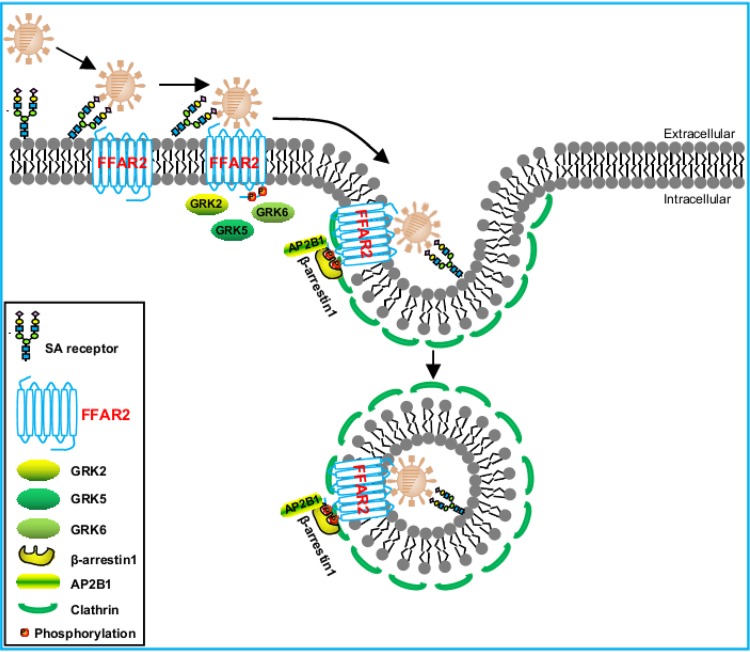
FIG 10.
Model of the role of FFAR2 in IAV entry into host cells. Upon initial binding with sialic acid on the cell surface, IAV binds to the FFAR2 protein, the C terminus of which is phosphorylated by the GRKs (i.e., GRK2, GRK5, or GRK6). β-Arrestin1 then translocates to the plasma membrane and interacts with FFAR2, followed by further interaction with AP2B1. Ultimately, the FFAR2–β-arrestin1–AP2B1 complex aids in the internalization of IAV via clathrin-mediated endocytosis.