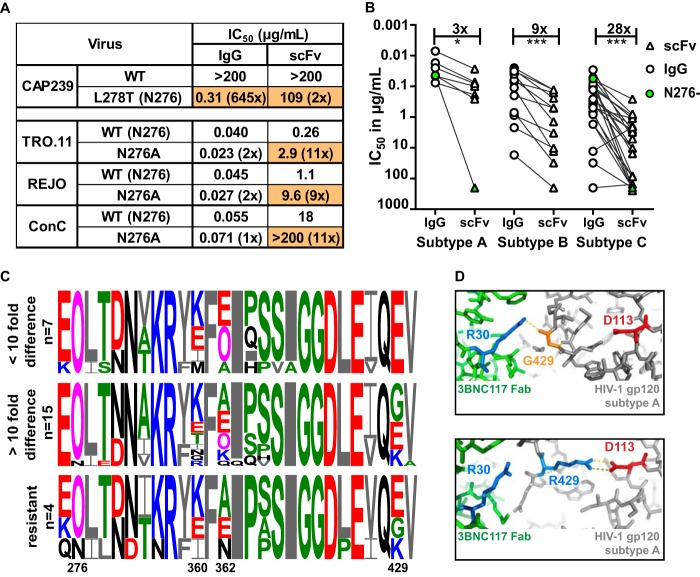
FIG 6.
Loss of potency for the 3BNC117 scFv was more pronounced for subtype C viruses. (A) IC50 of IgG and scFv neutralization of one virus that lacked the N276 glycan with a glycan knockin (CAP239) and 3 viruses in which the N276 glycan has been deleted (scFv corrected for molecular weight difference). Fold changes compared to the wild type are shown in parentheses, with changes of >5-fold colored in orange. (B) IC50 titers in micrograms per milliliter of IgG (circle) and scFv (triangle) against HIV-1 subtypes A, B, and C. Viruses lacking an N276 glycan are colored green. IgG- and scFv-resistant viruses are excluded. Fold differences are indicated above the graph and excluded the 2 viruses that lacked an N276 glycan. (C) Logogram of amino acid sequences of the CD4 binding site of HIV-1 subtype C viruses neutralized at the same level by scFv and IgG (<10-fold), those less well neutralized by scFv (>10-fold difference), or those resistant to both IgG and scFv. The N276 glycan and sites 360, 362, and 429, which exhibit the most variability, are indicated. Negatively and positively charged residues are colored red and blue, respectively. (D) Structural representation of the interaction of 3BNC117 Fab (green) and HIV Env (gray) containing an arginine (blue) or glycine (orange) at position 429. The aspartic acid at residue 113 in the HIV trimer is colored red, whereas the arginine at position 30 in the Fab is colored blue. Polar bonds are indicated by dotted lines (PDB entries 4JPV and 5V8L) (78, 79).