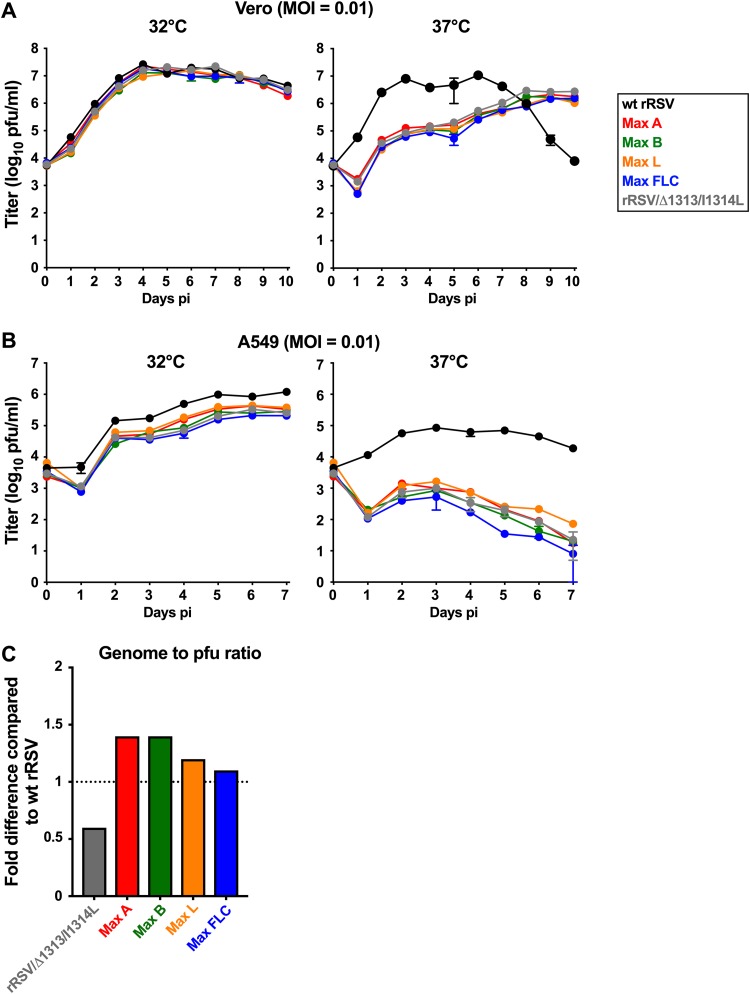
FIG 2.
Replication of CPO rRSVs and specific infectivity (genome-to-PFU ratio) of virus stocks. (A and B) The multicycle growth kinetics of wt rRSV, rRSV/Δ1313/I1314L, and the CPO rRSVs were assessed in Vero (A) and A549 (B) cells. Replicate cell monolayers were infected with wt rRSV, rRSV/Δ1313/I1314L, or the CPO rRSVs at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 and incubated at 32°C (left) or 37°C (right). Duplicate monolayers per virus were harvested daily from day 1 to 10 (Vero cells) or day 1 to 7 (A549 cells): the cells were scraped into the medium and vortexed for 30 s to release cell-associated virus, clarified cell culture medium supernatants were flash-frozen, and later titers were determined in parallel by immunoplaque assay in duplicate in Vero cells at 32°C. The results are expressed as mean values with standard deviations (SD) (note that for most time points, the SD value is so small that the its bars are not distinct from the filled circle marking the time point). The MOIs of the inocula also were confirmed by titration. (C) Specific infectivity. The genome-to-PFU ratios of CPO rRSVs, compared to those of wt rRSV and rRSV/Δ1313/I1314L, were evaluated by RT-qPCR. RNA was extracted from virus preparations, aliquots representing approximately 2 × 104 PFU of each virus were subjected to RT using a primer in the M2 ORF specific to genomic (negative-sense) RNA, and then 10% of each cDNA reaction mixture was amplified by a genome-specific qPCR. The results are expressed as fold difference compared to wt rRSV.