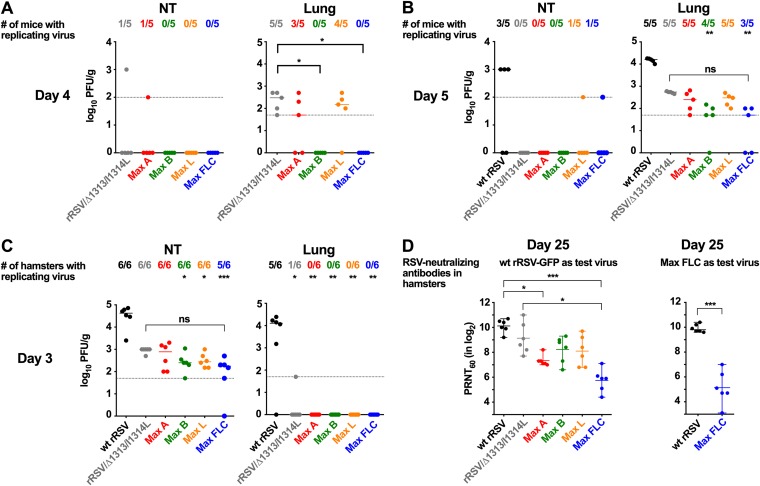
FIG 7.
Replication and immunogenicity of CPO rRSVs in rodents. Replication of CPO viruses was evaluated in the respiratory tracts of 6-week-old BALB/c mice (A and B) and 6-week-old golden Syrian hamsters (C), and immunogenicity was investigated in hamsters (D). (A to C) Groups of 10 mice (5 mice for wt rRSV) and 12 hamsters were inoculated i.n. with 106 PFU of the indicated virus per animal. On days 3 (hamsters) (C), 4 (mice) (A), and 5 (mice) (B), virus titers in the nasal turbinates (NT) and lungs were determined. The limits of virus detection, indicated by dotted lines, were 100 and 50 PFU/g for the NT and lung specimens of mice, respectively, and 50 PFU/g for the NT and lung specimens of hamsters. The number of animals per group with detectable virus is indicated along the top. (D) Serum RSV-neutralizing antibodies at day 25 in hamsters (6 hamsters per group). The 60% plaque reduction neutralizing antibody titers (PRNT60) were determined using wt rRSV-GFP (left panel) or Max FLC (right panel), as indicated. In panel A (right panel), brackets labeled with asterisks compare rRSV/Δ1313/I1314L with Max B or Max FLC. Note there are no data for wt rRSV in panel A. In panels B (right panel) and C (left panel), statistical differences for several viruses versus wt rRSV are indicated by an asterisk(s) located under the number of mice or hamsters with replicating virus. In addition, in panels B (right panel) and C (left panel), brackets indicate a lack of significant difference (nonsignificant [ns]) between rRSV/Δ313/I1314L and Max FLC. In panel D, brackets labeled with asterisks indicate the significance of differences between wt rRSV or rRSV/Δ1313/I1314L and the indicated viruses *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.